Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of storage, computer memory, and processing power. It includes networking, servers, software, storage, databases, analytics, and intelligence. All resources are delivered over the internet thus called cloud computing.
In order to understand his concept of cloud computing thoroughly and simply, let's break down the term into two. First, understand what the cloud means in technology. In simple terms, you can say that the cloud is a synonym for the World Wide Web or the Internet, but instead of providing access to the websites, the cloud allows you to access & use the software.
Now let’s move on to computing. Compute refers to the resources that are going to be used for the successful operation of the cloud-based software. For example, if you are using a 3D-graphic rendering application, then it definitely requires hardcore CPUs, RAM, GPUs, etc. This hardware is called computing resources.
In a nutshell, we can say that cloud computing is anything that involves providing computing services over the cloud. Some of the most popular cloud computing companies’ examples are Salesforce, Digital Ocean, AWS (Amazon Web Services), Dropbox, etc. Even a gaming company like Ubisoft is exploring new grounds for cloud computing. We are going to discuss more of that in the coming sections.
What are Cloud Computing Benefits?
Cloud Computing is flourishing in every sector and becoming popular in every industry, size, and sector. The way of utilizing cloud computation differs from company to company. Some might use it for database backups only and there are some companies that use clouds for providing their Software-as-a-Service or SaaS.
Case Study: Adobe is a computer software company that primarily provides creative software products. You may have heard some of them like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Acrobat Reader, and Adobe Creative Cloud. Initially, they used to sell on-premises software to each customer. But it was leading to software infringement and they were making huge losses. To overcome this problem, they entirely moved to cloud computing and started providing all their applications in their Adobe Creative Cloud. Now the users can access their software as a service.
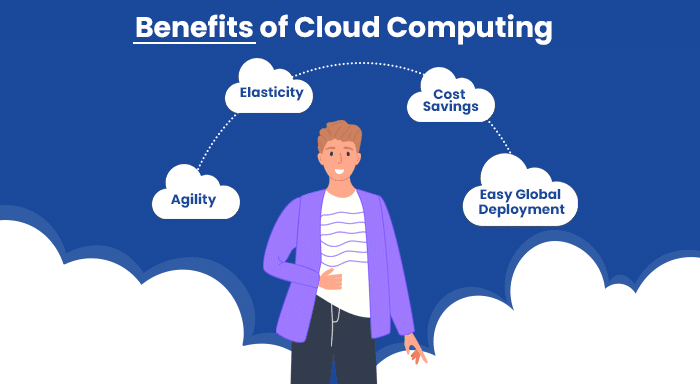
Without further ado, let’s have a look at the benefits of cloud computing.
- Agility: Since the introduction of clouds, people don’t need to think twice about creating something because they have one less thing to worry about i.e. owning and managing servers. As the technology has strengthened more and more, cloud computing is not limited to the remote servers only, there are other companies that provide other infrastructure services like computing, storage, and databases, to the Internet of Things, machine learning, data lakes, and analytics, and much more. Because of this, we have seen the birth of the term “As-a-service”, whether it’s a software as a service or environment as a service.
- Elasticity: Being Scalable, if not the best, is surely one of the most important benefits of cloud computing. Nowadays, most businesses are dynamic and their need for resources goes up and down drastically. In this case, cloud computing is an ideal solution because it can deliver resources as per the latest business requirements. It allows businesses to run their operations at their own pace without thinking much about resource scaling.
- Cost Savings: There are some clear cost-cutting; (i) Don’t need to buy hardware. (ii) Don’t need to develop software or purchase one. (iii) No need to set up servers and data centers. These are the only few that I have mentioned.
- Easy Global Deployment: Expanding your business around the world is also easier when you have the support of the cloud infrastructure. For instance, AWS (Amazon Web Services) provides its cloud computing services to McDonald's, Netflix, Twitch, etc, allowing you to launch your services in most geographical locations on the earth within a few clicks. So literally, there are no boundaries for any businesses that are utilizing the cloud.
Types of Cloud Computing
Now you have understood the fundamentals of cloud computing and its benefits, let us move on to the next part, i.e. its types.
Essentially, there are four types of cloud computing and we are going to explain each of them below.
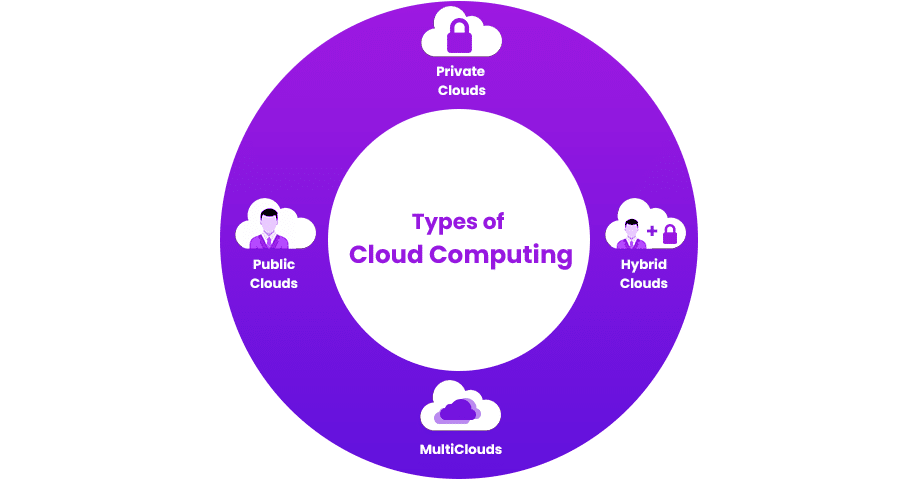
Public Clouds
Most of the cloud services providing companies you may have heard of are public cloudsYou can hire a custom Salesforce software developer, as well as Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM Cloud, Google Cloud, Alibaba Clouds, or Oracle Cloud programmers to create cloud solutions. There is one thing common between these platforms, which is that all the owning entities develop the infrastructure and the end-users of their services don’t own the clouds.
Apart from this, there are some public cloud service providers that even provide on-premise data centers. In essence, we can say public clouds are those that have multiple tenets. All the examples we mentioned above are paid services, but there is one cloud provider (The Massachusetts Open Cloud) that allows you to use the cloud free of cost. So this clears the fact that Fee Structure is not a contributing factor in being a public cloud.
Private Clouds
In contrast to the public, private clouds are owned by the end-users or a group(s). In general, the end-user's firewall protects these clouds. Traditionally, all the private clouds were on-premises, but recently, we have seen private clouds that were rented or owned by vendors in remote locations. Despite this, the end-user still has ownership. Considering this additional aspect, now the private cloud is a subcategory even further.
- Managed Private Clouds: Deployed, managed, and Configured by third-party vendors. Some businesses prefer to keep their distance from this type of cloud because they lack integrity.
- Dedicated Clouds: This is a cloud within a cloud. Let me break this up for you. Suppose your entire company has a cloud for its operations and with this, the accounting department has its own dedicated cloud. When using private or dedicated clouds, it's crucial to optimize system performance to avoid issues such as CPU throttling and check temperature, which can occur under heavy workloads, potentially affecting your cloud's efficiency.
Hybrid Clouds
In a nutshell, a hybrid cloud is an “integrated cloud” combination of two or more clouds that are connected via LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network), VPN (Virtual Private Network), or APIs (Application Programmable Interface).
You can say hybrid clouds are one of the most complex as compared to others. This is because every business builds its hybrid clouds as per its requirements. I gave some of the common solutions below.
- 1 Public Cloud and 1 Private Cloud
- 2 or more private clouds
- 2 or more public clouds
- A Bare Metal (System Without a base Operating System) environment, and a virtual environment.
Even though hybrid clouds are a combination of multiple clouds, they are managed and maintained as a single environment.
Multiclouds
Multiclouds, as the name suggests, are built by combining more than one cloud from different vendors. These vendors either could be public or private clouds.
Multiclouds and Hybrid clouds may sound the same, but there is a key difference. A hybrid cloud needs to be treated as a single cloud and it is managed by using some integrated management and orchestration platform. Apart from this setup, all clouds that are made by combining two or more clouds are simply multiclouds.
It suggests Hybrid cloud is the subdivision of Multicloud.
Cloud Computing Example We Use in Real-Life
Some of the world’s largest tech giants offered these cloud services and, I am quite sure, most of us have used these. Let’s have a look.
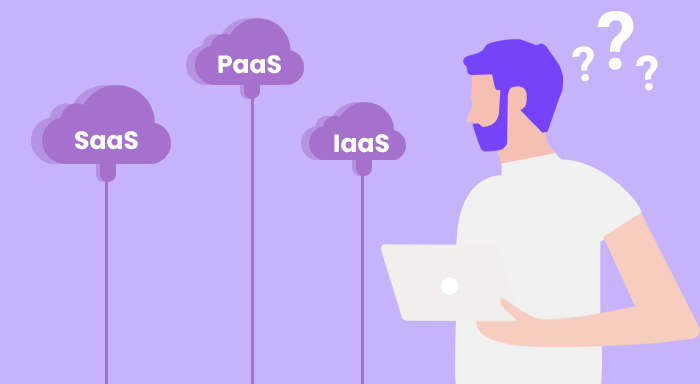
- SaaS (Software as a Service)- These are cloud-based applications or software that is hosted in the cloud. People can access it via a web browser, an application, a mobile operating system, etc. It has available on paid subscriptions. For accessibility of new features, there is no requirement to upgrade the system, new features are available as soon as they are added. Data won't be loosing if anything happens to the device as data is stored in the cloud. SaaS models are used in most commercial setups today and also in many AI-based softwares.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)- It provides an on-demand platform like hardware, infrastructure and development tools, complete software stack, etc for the development of software. This helps in running, developing, and managing software without the cost and management of a platform. With the help of PaaS, it is possible to host everything like servers, networks, operating systems, and databases. Now PaaS is built around containers. Containers are virtual models without the requirement for servers. For example, Red Hat OpenShift is a popular PaaS built on a Docker container.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)- It provides access to computing resources, like servers, networks, storage, etc over the internet on a demand basis. This reduces costs and purchasing ample resources.
- FaaS (Function as a Service)- It allows one to build, run, execute, and manage functions without having any infrastructure. It is an execution model. FaaS solutions are available on public clouds It makes functions available via API hence functions arent resource or event-driven.
Comparison with Example
| Platform | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| SaaS | Software as a Service: These are software applications provided on the internet by third-party vendors. | Google Workspace, Dropbox, Salesforce, Slack, HubSpot, GoToMeeting |
| PaaS | Product as a Service: They are also known as cloud platforms because they deliver both hardware and software over the internet. | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku, Adobe Magento Commerce Cloud, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos, OpenShift |
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a Service: These are the cloud-based alternatives to most traditional on-premise resources like storage, networking, virtualization, etc. | DigitalOcean, Linode, Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE) |
| FaaS | Function as a Service: This is the serverless method of executing a code written by the developer. Here, you need to store the code on the FaaS application and an event will automatically execute it. | IBM Cloud Functions, Amazon's AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Microsoft Azure Functions (open source), OpenFaaS (open source) |
Uses of Cloud Computing in Everyday Life
- Video streaming platforms
All video streaming platforms are the application of cloud computing. This has only made it for users to have affordable services while providers use expensive hardware and software. They have recovery technologies to correct any transmission errors which hampers the flow of the video stream and keeps it synchronized.
- File hosting services
Uploading and downloading files is also an application of cloud computing. Most storage services are based on cloud models which are used for data storage and creating backup copies. Users can access and control files remotely, and synchronize files across multiple devices. By synchronization of data, it will be updated at all times.
- Backup solutions for systems, sites, and software
Many systems used for backup are now based on cloud computing. This eliminates the requirement for repetitive manual backup operations. Due to this, it is possible to have secure backup copies regularly, without any manual effort.
- Chatbots
Advanced algorithms in cloud computing can create chatbots. It has the ability to directly communicate with a virtual operator when someone inputs something. Companies use it a lot for their customer service where customers' queries and problems are resolved. Other examples are FAQ page, proposal, Contact us
page, etc.
- Social Media
Social networking sites use cloud platforms to store their user's content. This reduces the costs related to data backup and recovery.
- Online Shopping
Online shopping websites use the cloud to store the details of their users. That is how you always get suggestions based on your preferences. For smooth buying
and payment, they let you mark items as favorites and save your card details.
- Education
Online courses are applications of cloud computing only. The data and content materials are stored in cloud platforms only. This enables students to access those contents anytime and anywhere. This is allowing distance learning to be possible. Also reducing costs and accessibility in remote areas. This is enabling educational institutions to offer more courses.
- Storing Data
Nowadays the use of cloud platforms for storing data is increasing. It keeps your data safe and secure and can be accessed anytime and anywhere.
- Data Analytics
Extremely large amounts of data cannot be stored and analyzed in traditional data management systems. But the cloud has unlimited data storage capacity due to which large amounts of data can be stored as well as analyzed. Specialized big data services can help organizations effectively leverage cloud technologies to transform massive datasets into actionable insights and strategic advantages. Now data handling isn't a problematic task for companies.
- Testing and Development
Earlier testing and development were very time-consuming, expensive methods that required extravagant infrastructure and manual efforts. With the cloud, you get scalable and flexible services where data can be tested and developed very easily.
- Antivirus applications
Antivirus software is stored in the cloud through which any kind of viruses, bugs, and errors in the system can be spotted, and corrected. Now you don't need to install additional antivirus software for fixing viruses.
- E-Commerce platforms
Cloud platforms stores and manages customers' data. Hence reduce the time and manual efforts of organizations. Also with the usage of cloud platforms interaction between representatives and customers has become very easy.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is spreading its wings and new technologies like Metaverse are just an additional boon. For instance, Ubisoft, one of the biggest gaming companies in the world, has recently announced its own cloud computing project called Ubisoft Scalar. It is apparently going to be the biggest ever game world people have ever seen. While giving a sneak peek of Scalar, Ubisoft talked about the capabilities: "the construction of gigantic game worlds at a scale far greater than anything that's come before" and support "massive numbers of assets, simulations, AI and player entities". I believe we have only seen the tip of the iceberg. There will be way more depth and influence of this technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
The 4 types of cloud computing are private cloud, public cloud, hybrid cloud, and multicloud.
The cloud computing example that you can see in the real world are Gmail, Dropbox, Salesforce, DigitalOcean, Linode, Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), etc.
Cloud computing can be used for providing software, product, or even infrastructure as a service. Cloud can also be used as a software development environment for DevOps teams. Big data analytics is another one of the most common uses of cloud computing.
The 3 types of cloud storage are Object storage (for storing unstructured data), File storage (For storing hierarchical folders and file format), and Block storage (For storing data in the form of blocks with each block having its unique identifiers).
Also Read
Communication Protocols In IoT | How Do IoT Devices Interact?
Learn the Ideas Behind the Logical and Physical Designs of IOT
IoT Levels Explained: A Deep Dive into the Internet of Things Hierarchy
SuiteCRM Cloud Services with Suite On Demand
The Evolution of Cloud Computing: Latest Trends in the Technology Shaping The Future








