TwiML is Twilio Markup Language that helps businesses looking to incorporate sophisticated communication capabilities into their systems. As businesses increasingly depend on automated messaging and voice systems, becoming familiar with TwiML is important for business professionals and developers alike. This complete article explores the main concepts, functionalities, and practical use cases of TwiML in contemporary communication infrastructure.
What is TwiML?
TwiML, short for Twilio Markup Language, is an XML-based language that tells Twilio what to do during various events such as outgoing calls or incoming calls, MMS messages, or SMS messages. For example, when someone calls on your Twilio number, Twilio searches for the URL associated with the contact number and sends a request.
The Twilio Markup Language works as a link between Twilio’s communication platform and your application. Instead of needing complicated programming logic, TwiML enables developers to create user-friendly XML documents that contain simple instructions for managing numerous communication situations.
Let us take a basic example that showcase a standard TwiML structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Response>
<Say>Hello! Welcome to our automated system.</Say>
</Response>Main Features of TwiML
TwiML works on numerous basic principles that make it both robust and accessible:
- XML-driven structure: Utilizes simple XML syntax for smooth implementation
- Event-based responses: Responds to particular triggers such as messages or incoming calls.
- Platform agnostic: Compatible across distinct programming framework or languages.
- Scalable architecture: Manages all aspects ranging from straightforward responses to complex workflows.
The markup language removes the necessity for vast server-side logic by providing predetermined instructions that Twilio can understand and implement automatically.
TwiML Important Components and Structure
Comprehending the structural elements of TwiML is vital for successful implementation. Language involves two main components that interoperate to ensure complete communication workflows.
TwiML Verbs and Nouns
TwiML verbs describe all the actions that Twilio must perform, while nouns give additional data or context for such actions. Verbs are set of actions that you want Twilio to take like address the call by offering a warm greeting or send an SMS as a reply to an inbound message.
The following points give a list of TwiML verbs:
- Say: Convert a text to speech to engage in voice calls.
- Play: Plays audio during calls.
- Gather: Collects the input of the user via speech or keypad.
- Dial: Dials a call to a phone number.
- Record: It records the audio during the calls
- Message: Sends MMS or SMS responses to the customers.
- Redirect: It automatically transfers control to a different TwiML document
The following example showcases distinct verbs in action:
<Response>
<Say>Thank you for calling our support line.</Say>
<Gather action="https://yourapp.com/handle-input" numDigits="1" timeout="10">
<Say>Press 1 for sales, press 2 for technical support.</Say>
</Gather>
<Say>We didn't receive your input. Goodbye!</Say>
</Response> XML Structure Needs
TwiML elements including nouns and verbs have case-sensitive names. For instance, if you use instead of , the system will show an error. The name of attributes is also camelCased and case sensitive.
The proper structure ensures that the execution is reliable:
- All TwiML documents must start with a element.
- Verbs are sequentially executed from start to finish.
- It is important to ensure case sensitivity and proper XML formatting.
- Attributes ensure further configuration options for every verb.
An example of an effective TwiML structure with attributes is as follows:
<Response>
<Say voice="alice" language="en-GB">Hello from London!</Say>
<Play>https://yourserver.com/audio/welcome.mp3</Play>
<Dial callerId="+15*********" timeout="30">+1**********</Dial>
</Response> Using this structured approach to TwiML and Twilio API integration for voice calls makes sure that there is consistent and predictable behavior across distinct execution scenarios.
What Are TwiML Use Cases and Applications?
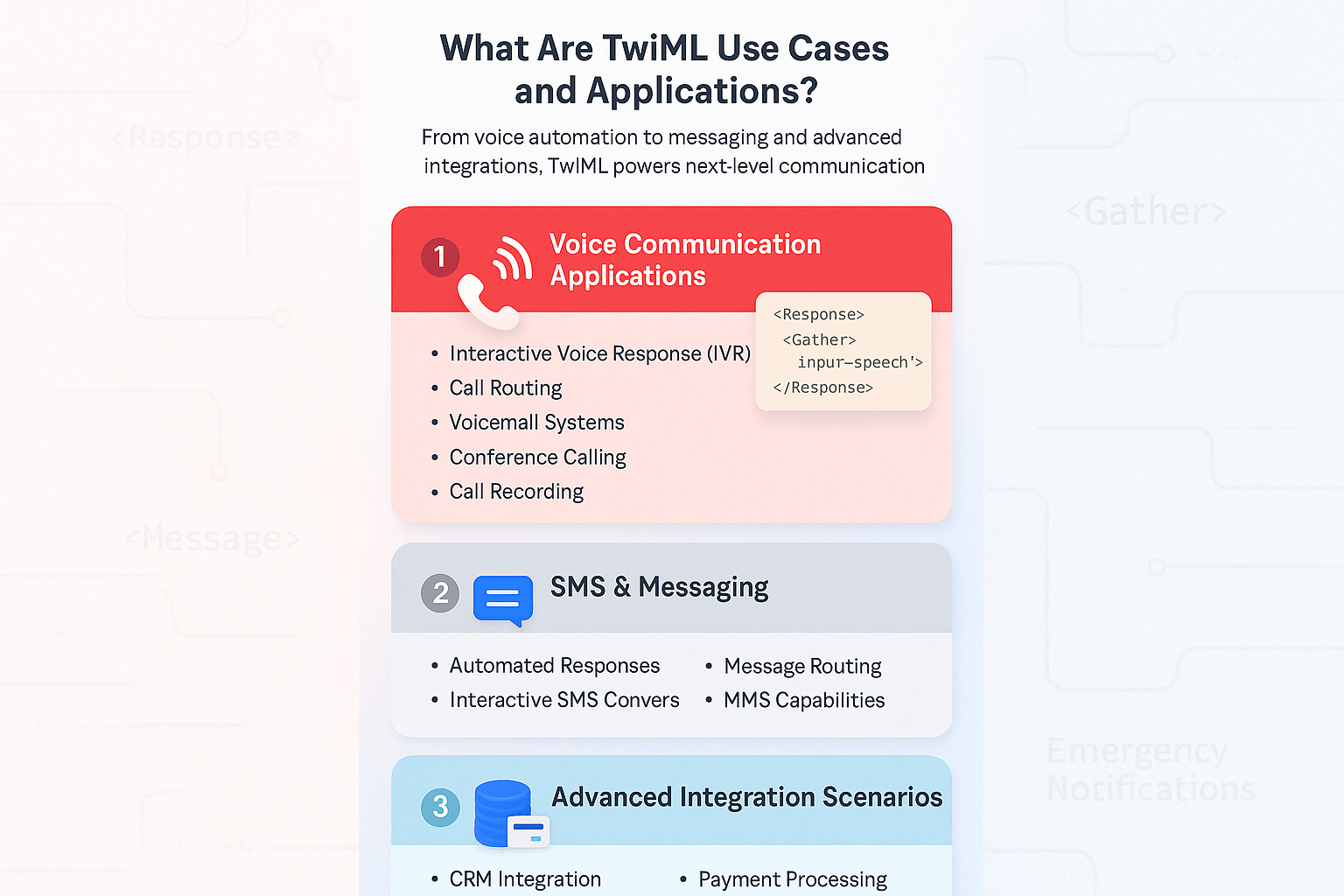
The usefulness of TwiML extends across diverse business applications, ensuring that it helps businesses of all sizes. From straightforward automated responses to advanced voice response systems for complex interactions, TwiML ensures the right fundamentals for advanced communication workflows.
Voice Communication Applications
TwiML is quite effective in providing dynamic voice experiences that improve overall customer engagement.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): Create advanced menu solutions for smooth customer service.
- Call routing: Direct calls to relevant agents or departments as per the input.
- Voicemail systems: Automatically record as well as manage customer messages.
- Conference calling: Connect multiple parties on a call and ensure a conference experience.
- Call recording: Record conversations for the purpose of training and quality assurance.
This is the main example of a comprehensive IVR system via TwiML:
<Response>
<Gather action="https://yourapp.com/ivr-handler" method="POST" numDigits="1">
<Say>Welcome to ABCD Corp. Press 1 for sales, 2 for support, or 3 for billing.</Say>
</Gather>
<Redirect>https://yourapp.com/ivr-fallback</Redirect>
</Response> SMS Applications and Messaging
The Twilio platform offers TwiML for complete messaging solutions:
- Automated responses: Send instant responses to all incoming messages.
- Interactive SMS conversations: Create conversational text-driven customer service.
- Bulk SMS Campaign: Ensure bulk sending of promotional content as well as notifications.
- MMS capabilities: Send as well as receive multimedia messages.
- Message routing: Route direct messages to relevant handling systems.
The following line of code demonstrates an example of TwiML in SMS messaging:
<Response>
<Message to="+1**********">
Thank you for your inquiry! We'll respond within 24 hours.
</Message>
<Message>
For immediate assistance, call us at 1-***-SUPPORT.
</Message>
</Response> Note: Having knowledge of what is the Twilio platform and how it enhances your experience ensure you have better context for improving TwiML effectiveness.
Advanced Integration Scenarios
Various enterprises leverage TwiML for advanced automation workflows:
- CRM integration: Associate communication events with relevant customer records.
- Payment processing: Manage secure transactions via text or voice.
- Appointment scheduling: Automate confirmation of bookings as well as reminders.
- Emergency notifications: Deliver crucial alerts across diverse channels.
- Feedback and survey collection: Collect input of customers via automated platforms.
Implementation of Right Practices
Effective TwiML implementation needs close focus on numerous important factors that ascertain optimal user experience and performance. Such practices have evolved via community feedback and extensive real-life applications.
Optimization of Performance
Effective TwiML design impacts operational expenses and user experience directly:
- Optimization of Response Time: Ensure that TwiML documents are well-structured and lightweight.
- Management of Errors: Execute fallback options for all the failed processes.
- Testing protocols: Rigorously check all the TwiML workflows before execution.
- Tracking Platforms: Monitor user interactions and performance metrics.
- Scalability planning: Create workflows that manage growing call volumes.
Security Considerations
Courtesy of TwiML Bins, you get the capability of hosting any appropriate TwiML directly with Twilio. Furthermore, Twilio can manage scaling and hosting as you are launching your app. However, security remains one of the main requirements:
- Authentication mechanisms: Assess webhook requests directly from Twilio.
- Data protection: Secure confidential data in all TwiML responses.
- Access controls: You can put an authorization limit for who can actually make changes to your TwiML apps.
- Audit trails: You can ensure consistent logging of all your TwiML interactions.
- Compliance needs: Ascertain compliance to industry regulations and standards.
Development Workflow
Implementing efficient development practices simplifies TwiML execution:
- Version control: Systematically monitor changes made to the TwiML documents.
- Management of Environment: Separate testing, development, and production environments.
- Ensure Documentation standards: Ensure precise documentation for all TwiML workflows
- Team collaboration: Allow different developers to collaborate on the same TwiML projects.
- Deployment automation: Execute consistent integration for all updates related to TwiML.
TwiML Voice Flow Example
Incoming Call Flow

Fig: TwiML Incoming Call Flow
The Incoming Call Flow details the comprehensive steps that Twilio performs when a customer dials your Twilio contact number. Let us understand the breakdown of the detailed steps:
- A Client Calls Your Twilio Number
Any customer initiates the calling process by calling your Twilio contact number. - Twilio Then Receives the Customer’s Call:
Twilio detects that there is an incoming call request and instantaneously checks the Webhook URL set up for that Twilio number. - Webhook Request Sent to Your Server:
Twilio transfers a HTTP request (generally POST/GET) to the server of your application. Then, the server can respond with specific TwiML instructions. - The server replies with TwiML instructions:
Your application then creates a TwiML response. This can inform Twilio to:
<Say> a greeting.
<Gather> caller’s input. (for e.g., IVR menus).
<Dial> another Twilio number or any SIP endpoint.
<Record> the message for voicemail. - Call Execution:
Twilio sequentially implements the TwiML instructions. For instance, it can offer a welcome message to the caller, route the call to a human agent, or even record the message for later response.
- Response Management:
If an error occurs or no input gets received, Twilio can utilize fallback actions like <Redirect> to a different TwiML document.
Examples of Use Case: Call routing, customer support lines, IVR menus, voicemail systems.
Outgoing Call Flow
Fig: TwilML Outgoing Flow for Outgoing Calls Case 1 and Case 2
Case 1:
The Outgoing Call Flow showcases how an application can initiate calls programmatically via Twilio’s API
- Application Starts a Call Through REST API:
Your server first makes a request to the Twilio’s Calls API, specifying the ID of the caller, the number of the recipient as well as a TwiML URL. - Twilio then Places the Call:
Twilio dials the phone number of the recipient via the given parameters. - Recipient Chooses to Answer the Calls:
When your recipient decides to pick up your call, Twilio then immediately makes a request to the given TwiML URL. - Webhook Request to Server:
Twilio transfers an HTTP request to the endpoint of your application to fetch the TwiML instructions. - The Response of Server Via TwiML:
The server then chooses to respond with TwiML that determines what must happen during the call like:
<Say> a pre-defined automated message.
<Play> a recorded audio file.
<Gather> user’s input (for e.g., press 2 to connect to human agent)
<Dial> another conference or person. - Call Execution:
Twilio implements the TwiML instructions in real time, ensuring a smooth outbound communication experience.
Use Case Examples: Delivery confirmations, appointment reminders, customer surveys, and call notifications.
Case 2:
The Outgoing Call Flow – Case 2 showcases what should happen when Twilio tries to dial an outbound call, but the recipient chooses not to answer it, or the call fails.
- Application Starts the Call Via Rest API:
Same as before, your server transfers a request to the Calls API of Twilio, specifying recipient’s number, caller ID, and a TwiML URL. - Twilio Dials the Call:
Twilio places the call on the phone number of the recipient considering the given parameters.
Recipient Chooses Not to Answer Your Call or the Call Does Not Connect
There can be numerous reasons why Twilio cannot reach the customer: the call does not get connected due to line or network issues or the customer chooses not to pick up the call currently.
- Call Status Callback to Server:
Twilio transfers a HTTP status callback (if configured) to your app, keeping you informed about the outcome (e.g., busy, no-answer, or failed) - Optional Server Action:
Depending on the callback information, your application can easily:
You can retry the call after a fixed interval.
Go for SMS fallback via <Message>
Record the failure of analytics or reporting.
Use the alternative routing (e.g., Try another number). Final Outcome
In case 2, the Twilio call attempt ends without interaction with the client. However, your application can then decide the next course of action on the callback details.
Conclusion
TwiML offers an accessible and powerful approach to executing smooth communication features within contemporary applications. Its XML-driven structure integrated with robust infrastructure of Twilio allows developers to create complete messaging and voice solutions without extensive expertise on telecommunications.
The smart execution of TwiML can greatly improve customer engagement, simplify business processes, and ensure scalable communication infrastructure. From straightforward automated responses to advanced interactive systems, TwiML provides the functionality and flexibility needed for the dynamic business environment of today.
Organizations relying on TwiML execution must gain accessibility to enterprise-level communication capabilities while ensuring cost-effectiveness and simplicity that modern businesses require. As communication technology evolves continuously, TwiML ensures a strong foundation for creating profound customer experience solutions.
Learn More: Check out more informative blogs on our website. To integrate Twilio into your CRM, try only professional services and advanced plugins like Twilio SMS for SuiteCRM and Twilio Auto Dialer for SuiteCRM.








