When you are exploring the digital world, there is a good chance that you might have come across automation behind the scenes without even realizing it. Examples include search engines that automatically update results over time; someone using a customer service widget to get help or suspicious activities that don’t let your website run smoothly — all these examples involve bots. But what are bots?
In simple terms, bots are software programs that are designed to complete tasks automatically without needing any human interventions. With the rise of bots in recent years, they have become a core part of how the internet works; that is by managing tasks that would otherwise require a million humans to perform them manually. However, not all bots are built equal: while there are bots that benefit us, others can cause damage if used in an unethical or uncontrolled manner.
This article will discuss what bots are, their major categories, how they operate, real-world examples, benefits and risks associated and why managing them is essential for modern digital businesses.
What Are Bots?
When users ask about the meaning of bots, the answer revolves around the use of software to automate processes. According to Cloudflare, a bot is a software application programmed to perform specific series of tasks automatically over a network like the internet. Bots follow instructions and keep executing tasks repeatedly, often much faster and more consistently compared to humans.
They can mimic or even replace humans. For example, they can navigate webpages or explore websites, interact with online systems, or provide information. Some bots are involved in conducting beneficial activities, such as providing information to customers and indexing webpages. In contrast, there are also many bots that are malicious and scrape data and attempt to breach security "firewalls" to gain access to sensitive information.
How Do Bots Work? Bot Functionality Explained
Understanding bots means understanding how they function under the hood. At their core, bots follow instructions written in code that enable them to perform tasks autonomously. These tasks may involve:
- Sending and receiving data across the web
- Simulating human actions through APIs or scripts
- Using machine learning to interpret text or speech
- Repeating set operations without fatigue
Most bots use standard web protocols, including HTTP or HTTPS, along with an API to connect to websites or other applications. Sophisticated bots, such as AI-powered chatbots, use various advanced methods like natural language processing (NLP), to understand and answer human questions. Developers can now create bots using ChatGPT and similar AI technologies to build intelligent conversational agents.
Types of Bots on the Internet
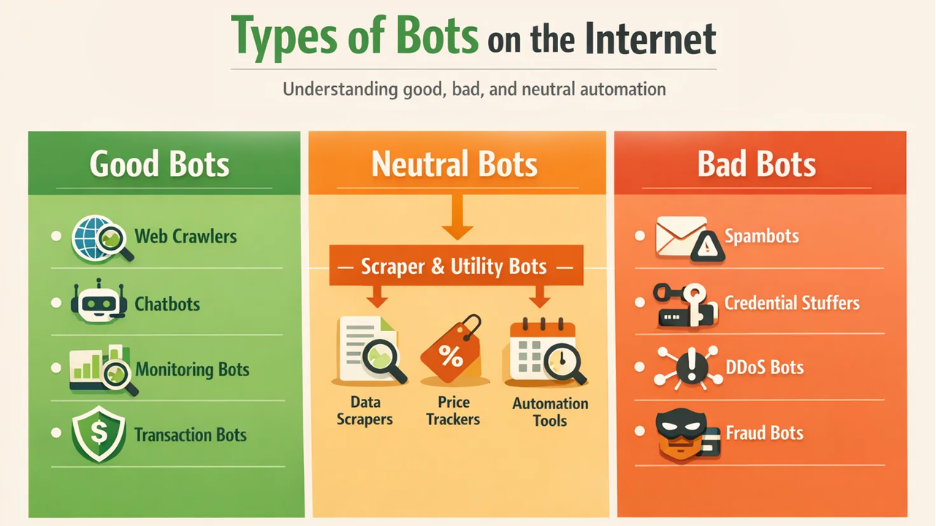
When defining bots, it’s helpful to distinguish the main types based on their purpose and behavior.
1. Good Bots: Helpful and Legitimate Bots
Good bots are designed to support useful and constructive activities online. These bots enhance user experiences and help businesses scale processes efficiently. Examples include:
- Web crawlers: Index web pages for search engines like Google and Bing.
- Customer support chatbots: Answer user questions and assist with navigation.
- Monitoring bots: Scan systems for uptime, security vulnerabilities, or performance issues.
- Transaction bots: Run checks and ensure proper handling of operations such as payments.
2. Bad Bots: Malicious and Harmful Bots
Bad bots operate with malicious intent or cause harm. They can degrade performance, compromise systems, or create unfair advantages, including:
- Spambots: Collect email addresses or post spam content.
- Credential-stuffing bots: Try stolen usernames and passwords.
- DDoS bots: Flood servers with traffic to disrupt access.
- Fraud bots: Mimic human actions to generate fake clicks or false data.
3. Neutral Bots and Utility Bots: Context-Based Automation
Some bots are not categorized as either good or bad. Their context and intent usually determine whether its activity is beneficial or harmful. Scraper bots are one such example. They can be used ethically for data analysis or unethically to harvest content. It depends on how they are used by users.
Common Examples of Bots in Everyday Use
To further explain how bots are used in everyday life, here are several real-world examples:
- Search engine bots scan and index the web to keep search results current.
- Shopping bots help users compare prices and find deals.
- Chatbots respond to customer inquiries on websites and apps. Specialized solutions like Auztron Bot provide targeted automation for specific business needs.
- Monitoring bots watch for anomalies in network traffic or system health.
- Social bots on platforms like Twitter can automate posting, liking, or retweeting.
These examples show how bots are used in everyday digital experiences.
Benefits of Bots for Businesses and Websites
Bots deliver efficiency, speed, and scalability by automating tasks that would otherwise require significant human time and effort.
Automation, Efficiency, and Operational Stability
Bots help automate mundane, repetitive tasks and can perform continuously without failure. Additionally, they can process massive amounts of work like indexing web pages or monitoring systems. They support digital platforms in a way that would not be possible by humans manually.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
One of the biggest benefits of using bots is that they have the ability to improve resource utilization and lower costs. Automating basic customer support, collecting data, and system checks can significantly reduce the amount of labor and time required by a human to perform routine tasks. Chatbots, for example, deliver instant responses to common inquiries. All this greatly improves user experience and reduces operating costs.
Data-Driven Insights and Decision-Making
Additionally, bots effectively collect, process, and analyze huge amounts of data. In marketing and analytics, bots can be used to track website traffic, verify advertisements, and measure user engagement. They also provide opportunities for further scalability and innovation, particularly when integrated together with AI to enable personalization and adaptive responses to user requests. Platforms like Botify AI exemplify how AI-powered bot solutions enhance automation capabilities.
Speed, Accuracy, and Real-Time Responsiveness
On top of that, bots typically provide faster speeds, better accuracy, and greater responsiveness than humans. With proper configuration, automated systems can handle large volumes of data at higher speeds and with fewer errors than traditional methods. They can detect problems with performance or locate potential security vulnerabilities via continual monitoring.
Common Use Cases of Bots Across Industries
Bots are used across industries to automate processes, improve user experiences, and support large-scale digital operations.
Search Engine Indexing and SEO
Search engine bots, also known as crawlers, navigate websites to identify and index webpages, so search engines can provide users with the most relevant and up-to-date results. This is a key component in how search engines and SEO function together.
Customer Support and User Engagement
Bots are used extensively for customer service and user engagement. Chatbots answers users' queries, assist them by guiding through processes, and provide continuous support on both websites and applications, improving user experience, and reducing operational costs for businesses.
Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention
Finally, bots play an important role in cybersecurity and fraud prevention. Security bots analyze behavior patterns to detect and block threats like credential stuffing or brute-force attacks, strengthening overall digital protection.
System Monitoring and Performance Management
Performance management and system monitoring are two more important use cases. Real-time traffic patterns, server health, and uptime are tracked by monitoring bots. These bots send out alerts in response to performance problems or anomalous activity, assisting businesses in staying dependable and reacting promptly. Teams also leverage chatbots for internal DevOps communication to automate alerts, incident responses, and team coordination.
Digital Marketing and Analytics
Bots also play a major role in digital marketing as they collect and analyze data, verify ads, and detect fraudulent traffic. By filtering invalid or fake interactions, marketing bots support accurate reporting and better campaign optimization.
Risks and Challenges of Bots
While bots offer clear advantages, unmanaged or malicious bot activity can create security, performance, and data-privacy risks.
Performance and Infrastructure Risks
Bots can lead to performance and infrastructure issues. Excessive automated traffic may overwhelm servers, slow down websites, and increase bandwidth costs, negatively affecting genuine users and overall system reliability.
Malicious Bot Activity
One of the primary risks associated with bots is malicious activity. Bad bots can engage in credential stuffing, spam distribution, content scraping, or denial-of-service attacks, posing serious security threats and potentially causing financial and reputational damage.
Data Privacy and Content Scraping Risks
Another challenge involves data privacy and content protection. Scraping bots can extract sensitive information or proprietary content without authorization, raising legal, ethical, and compliance concerns, particularly in regulated industries.
What Is Bot Management and Why It Matters
Understanding bots isn’t complete without discussing how to manage them. As Cloudflare explains, bot management involves identifying and controlling bot traffic, allowing helpful bots while blocking harmful ones. Proper bot management protects infrastructure, improves performance, and preserves the integrity of online services.
Bot management tools use techniques like behavioral analysis, CAPTCHA challenges, and IP reputation to differentiate between legitimate and malicious bots. For example, a bot manager might allow search engine crawlers through but block credential-stuffing bots that try to break into accounts.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding Bots Matter
Bots are a foundational element of the modern internet. They automate tasks that range from indexing web pages to engaging with users in real time. Bots encompass a diverse range of automated software programs that can be both beneficial and harmful depending on their purpose and implementation. Understanding what bots are, how they work, their benefits, and the risks they pose is essential for navigating digital environments effectively and securely.








