Introduction
In today’s ever-competitive business world, customer relationship management can be the difference between business success and failure. Operational CRM is quickly becoming an essential tool for those wanting to optimize customer-related business activities and deliver customers exceptional experiences. The role of an operational CRM system is to form the backbone of business in connecting sales, marketing, and customer service functions through automation.
This particular method of Customer Relationship Management targets optimizing everyday business processes rather than scrutinizing data or planning strategies. As a result, the process of automating everyday tasks, as well as gaining immediate access to customer data, allows teams to handle the demands of customers faster than ever before.
Comprehensive Summary of Operational CRM
Customer Relationship Management Basics Operational CRM primarily focuses on automating the core functions performed by sales, service, and marketing departments.
Core Business Functions These solutions enable the use of lead management, contact management, sales pipeline management, marketing automation, and customer service management.
Automation Benefits: The key differentiator of Operational CRM is processing automation, and it eliminates tasks by manually storing customer information in one place.
Business Impact: Organizations see increased productivity, higher customer satisfaction, better collaboration, and higher revenue as a consequence of optimized operations.
Practical Applications: Customer service departments utilize operational CRM to handle tickets, respond to customers, and track interactions.
Selection Strategy: Choosing the correct operational CRM solution is necessary from the viewpoint of its integration capabilities, scalability, user experience, and its alignment with the organizational objectives.
What is an Operational CRM?
Operational CRM refers to a type of Customer Relationship Management software used in automating various business operations involving marketing, sales, as well as service. Unlike other types, which have the ability to analyze or collaborate, Operational CRM software has capabilities limited to handling operations involving present or potential clients.
In essence, an operational CRM is a central repository through which customer data is accessed and moved between various departments in an organization. When a marketing department completes an acquisition of a new business lead, for example, when a new lead is captured, the data is automatically made accessible to sales teams. Once a sale is completed, customer service teams gain immediate access to the customer’s complete interaction history.
The operational orientation of these systems also ensures they focus on doing rather than analyzing. Though these systems help in acquiring important data, their usage lies in ensuring a smooth and optimized customer experience and not in analysis or preparing reports. Salesforce reports the average revenue increment and sales productivity enhancement of businesses using CRM as 29% and 34% respectively.
What Does Operational CRM Typically Support?
Three core business domains are supported by operational CRM systems: marketing automation, sales automation, and service automation. Specific features that improve client engagement and expedite workflows are advantageous to each region.
Sales Automation
An operational CRM offers many options to assist the Sales team. Operational CRMs offer the following features:
- Lead Management: The process of creating, tracking and developing potential customers from the time of first contact to closing the deal.
- Contact Management: Store all your customer/prospect information in a database for easy access and searching.
- Opportunity Tracking: Tracking your offers through the sales pipeline by taking action at each stage of the sales process.
- Quote Generation: Using technology to create professional quotes and proposals.
- Sales Forecasting: Determine potential future earnings by following the sales pipeline activities and historical sales patterns.
Marketing Automation
Marketing teams utilise operational CRM to manage and build relationships through:
- Campaign management: Planning, executing, and monitoring multi-channel marketing initiatives
- Email marketing: Sending tailored and targeted email communications to customers based upon their preferences and behaviours
- Lead scoring: Automatically ranking potential customers by their likelihood of becoming a paying customer
- Segmentation: Developing targeted audience segments so that relevant messages can be delivered to each segment
- Landing pages: Establishing and testing landing pages in order to acquire new leads
Service Automation
Customer service operations benefit from operational CRM through features that enhance support efficiency:
- Case management: Creating, assigning, and tracking customer service requests from submission to resolution
- Knowledge base integration: Providing agents and customers with self-service resources
- Multi-channel support: Managing interactions across email, phone, chat, and social media from one platform
- Automated routing: Directing inquiries to the most appropriate team member based on skills and availability
- Service level tracking: Monitoring response times and ensuring compliance with service agreements
What Makes Operational CRM Systems Different?
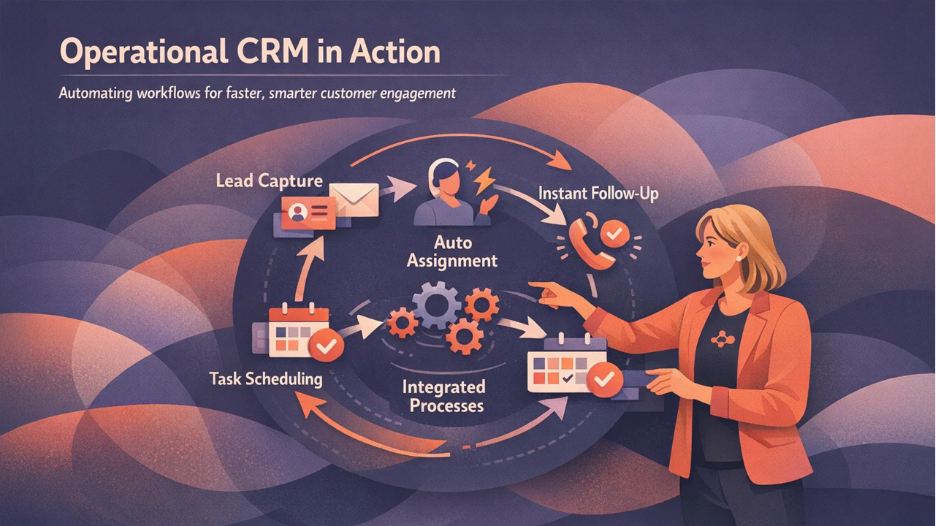
Operational CRM differs from other categories of CRM in focusing on the automation of processes, immediate access, and cross-functional integration. Whereas analytical CRM focuses on the analysis of data, and the collaborative one focuses on communication channels, operational CRM focuses on the efficiency of workflows.
Automation is the distinguishing mark of operational CRM. These systems automatically handle many tasks that would otherwise take away a portion of employee time. The moment a lead submits a web form, the operational CRM automatically creates a contact record, assigns the lead to a sales representative, sends a welcome email, and schedules a follow-up task. This process occurs instantly, without human intervention, ensuring that no opportunity is overlooked.
Another distinguishing factor is the focus on customer-facing processes rather than analysis for internal purposes. Although a lot of data is collected in operational CRM, the end objective is facilitation through the data. The data is used for decision-making in order to perform a task, such as accessing data to seed a campaign or to solve a case.
The integration capabilities that distinguish operational CRM are also worth mentioning. These tools integrate with emails, calendars, telephony, social media sites, and other applications to provide a comprehensive outlook on interactions. According to LinkedIn statistics, there is a 27% greater rate of customer retention for firms with an integrated CRM system.
Also Read - What Is Strategic CRM?
Benefits of Operational Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
By incorporating operational CRM, there are noticeable benefits reaped in all areas where the organization is operating. This includes increased efficiency, customer satisfaction, revenue growth, as well as teamwork.
Enhanced Productivity
Automation takes care of time-consuming manual processes, so employees have more time to pursue high-value activities. Sales people have more time to network since they dedicate less time to entering data. The marketing team completes more tasks quickly since all activities are automated. Service desk employees take less time resolving complaints since they have complete access to the customer record.
Improved Customer Experience
Operational CRM provides personalized and continuous interaction with customers through all possible touch points. If all team members gain access to the full set of customers’ information, the conversation will appear to be continuous and not disjointed. Repeated explanations by customers about themselves and their situations will not happen anymore. The time taken to reply will go down because of automated routing and prioritization of issues that require immediate attention.
Better Cross-Functional Collaboration
Removal of departmental silos leads to synchronization between the sales, marketing, and service departments. The marketing department is able to identify those campaigns that produce high-quality leads for the sales department. The sales department is able to determine areas where upselling needs to be done based on the information provided by the services department. The services department is able to notify the sales department of accounts that are about to expire.
Increased Revenue
Operational CRM contributes to the generation of income in a variety of ways. Lead nurturing automation results in the conversion of more leads into clients. Improved visibility of the sales pipeline enables the sorting of more significant opportunities by the sales force. Quick turnaround enhances the possibility of closure. Service automation translates to increased customer retention. The aggregate effect is quite substantial.
Data Accuracy and Consistency
Data is managed more accurately with a centralized system, minimizing errors and synchronizing efforts from a unified base. Duplicates decrease, entry errors are eliminated, and information is up to date. Access to accurate information streamlines decision-making within the organization. Customer service issues caused by outdated or inaccurate information are effectively eliminated.
Operational CRM Examples: Customer Service
Customer service is one of the applications that has the widest reaches when it comes to operational CRM, an area that has managed to change the face of customer service by automating, organizing, and making it accessible. Customer service teams use operational CRM software.
For example, a typical scenario involving the customer service process. The customer places a request for support through the corporate website. The operations CRM system instantly opens a case, assigns it a unique number, and directs the query to the corresponding group of employees depending on the nature of the problem. The automated system then delivers a confirmation message to the client.
When the assigned agent logs into the ticket, they get the entire history of the customer, including past purchases, past service interactions, current conversations with other departments, and related notes in the account. All these help the assigned agent to take informed and personalized actions without having to go back to the customer for information. If it warrants escalation, the operational CRM maintains all transitions and related audit trails.
Service Automation goes far beyond ticketing. Service operations can be automated by:
- Automatically suggest relevant knowledge base articles to agents and customers
- Trigger proactive outreach when system monitoring detects potential issues
- Generate satisfaction surveys immediately after case resolution
- Alert supervisors when tickets exceed response time thresholds
- Create follow-up tasks to ensure complex issues receive continued attention
In many companies, their operation CRM is integrated with live chat solutions, telephonic communication systems, and social monitoring services. This multi-channel service enables customers to receive excellent service no matter how they want to get in contact with the firm. Customers will not have to repeat their issues to different staff members since agents have everything in one place.
How to Choose Operational CRM Software
When selecting an operational CRM, you have to adequately analyze the business needs, technology, and expansion strategies you require, which affects business activities in various departments on a daily basis. Understanding the landscape of the different types of CRM systems is the first step toward making an informed decision that aligns with your organizational goals.
Assess Your Requirements
Begin with describing current business processes and points of pain in your sales, marketing, and service functions. What are the most time-intensive tasks? At which points do handoffs of customers go poorly? What kinds of data are in separate systems? Such pain points inform what will be most valuable in your operational CRM.
Evaluate Integration Capabilities
A CRM system is most valuable when it integrates effortlessly with other tools you are already using. Look at how a CRM might interface with your email program, calendar system, accounting program, and other software solutions. This type of integration will probably be more functional than an outside interface.
Consider Scalability
Select your operational CRM tools in such a way that they are able to accommodate your growing enterprise. Is your system scalable to handle larger amounts of data? Does it cost effectively to accommodate more users? Will it be able to accommodate more complex processes as your company changes?
Prioritize User Experience
An operational CRM system, no matter how functional, will fail if the workforce is unwilling to use it. Test it on the staff members for its usability. Is it easy to navigate? Is it easy to seek information? How user-friendly is it for working in the fields? User adoption, not functionality, is what matters.
Review Customization Options
Customized solutions will invariably include business-specific procedures, beyond the capabilities of generic CRM configurations. Evaluate how intuitive it is to customize fields, workflows, reports, and user interfaces, while carefully balancing flexibility against the added complexity that customization may introduce. In most cases, simpler configurations deliver better long-term usability.
Examine Support and Training
Success with implementation requires adequate training and ongoing support. What does the vendor provide in the area of resources? Is training comprehensive and accessible? Is technical support responsive? Consider also TCO, which involves training and support rather than just license fees.
Final Thoughts
In today’s rapidly accelerating and competitive world, the need for “Operational CRM” solutions becomes imperative to efficiently manage customers in today’s fast-paced environment. When core operations are automated and customer data is centralized, sales, marketing, and service teams can work more efficiently while delivering consistent, high-quality, personalized customer experiences. However, successful CRM implementation requires more than just technology.
It is vital that a business considering an operational CRM solution maps its workflows, identify inefficiencies in the current system, and rank desired functionalities by priority. By starting with core capabilities and adding over time, it's possible to ensure real, long-term adoption and success. As customer expectations continue to rise, operational CRM provides a competitive advantage by improving productivity, strengthening customer relationships, and supporting sustainable business growth in an increasingly competitive market.
Related Read - Collaborative CRM Tools









