Customer data is available everywhere—in sales tools, marketing dashboards, support systems, and even in spreadsheets. The traditional data management strategy failed to manage, analyze, and act on data when it’s fragmented. This is where data warehousing plays a crucial role in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. A CRM data warehouse collects and analyzes all customer information into a unified, structured system that helps businesses make informed decisions, identify trends, and monitor relationships. However, creating powerful data warehouses in CRM systems is essential to provide your team with a 360-degree view of the complete customer sales journey.
This comprehensive piece of paper will break down what they actually are, how they work, and why it matters to modern, growth-oriented businesses to drive sales and improve engagement.
Introduction to CRM Data Warehouse
A data warehouse is a common repository that consolidates client data from diverse sources and provides a single, centralized platform for storage and analysis. Compared to operational CRMs designed to automate routine tasks, a data warehouse in CRM systems focuses primarily on trend detection, predictive modeling, and complex data management. The goal of creating modern databases is to provide businesses with a centralized view of customer information integrated from multiple sources, like websites, chats, and social media interactions. This unified approach enables businesses to understand the customer pipelines better, analyze behavior, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
In the context of business success, Gartner's research states that businesses that integrate with CRM data warehouses experience a hike in customer satisfaction of over 23% compared to those depending on fragmented data systems.
Why Data Warehouses in CRM Systems Matter
In the data-heavy landscape, sales teams often risk losing deals when they relyon outdated CRM databases to manage customer data. Marketing campaigns miss the mark as they target the wrong audiences because product usage data sits in disconnected systems. And support agents are unable to see fixed issues, leaving customers frustrated and dissatisfied.
The issue here is not the technology—it's the lack of data visibility. Your business handles thousands of customer interactions every day, but siloed data leaves you with limited visibility.
A CRM data warehouse resolves these challenges by aggregating customer relationship information from every touchpoint into a comprehensive database built for analysis. This delivers insights on customer relationships, helping you better understand customers’ actions through historical data and future forecasting. Consequently, these measures result in a 30% improvement in decision-making efficiency and a 25% increase in customer retention.
Without a centralized database, small teams are more vulnerable to the risk of losing deals. However, an effective CRM for small businesses driven by CRM data warehouses helps them improve retention, enhance operational efficiency, and boost overall productivity.
How a CRM Warehouse Works
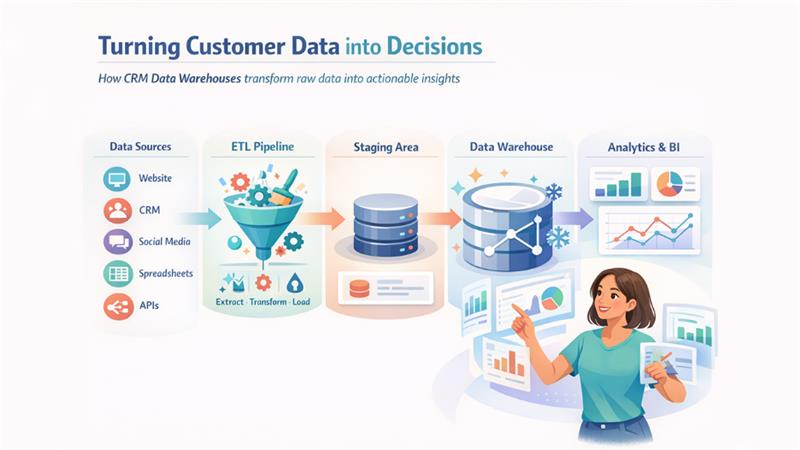
These steps demonstrate how a CRM data warehouse turns raw customer data into valuable, actionable insights, irrespective of whether you’re seeking a
- It gathers data from multiple platforms and customer touchpoints
- Stores, manages, and analyzes the data in a centralized database for quick access
- Applies data mining and big data analytics to identify trends, patterns, and correlations
- Provide extensive insights into customer behavior, preferences, and buying journeys.
- Enables businesses to use these insights to anticipate customer needs, find patterns, and make lasting decisions.
Architecture and Components of CRM Data Warehouse
The architecture of a CRM data warehouse follows a multi-layered approach designed to optimize the entire data flow from source to endpoints. Typically, flow goes through three main layers: ETL, data extraction from source systems, transforming into structured formats, and loading in repositories that support complex queries.
Data Sources:
These are the actual sources from which data is collected, like websites, transactional databases, social media channels, external spreadsheets, and CRM systems. The purpose of these systems is to provide raw, unstructured data to warehouses for storing, analysis, and reporting. Also, these source systems can be integrated with operational CRMs, like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Microsoft Dynamics, via database replications, file transfers, and API integration.
ETL Pipeline:
ETL, which stands for Extract, Transform, Load, is a process of extracting data from source systems, transforming it into standard formats, and loading it into data warehouses. This process helps cleanse, modernize, and deduplicate data before pipeline ingestion.
Staging Area
This space acts like a temporary storage zone designed to store raw data extracted from multiple sources before being moved for initial verification and quality audits. This helps identify potential risks in data records without hindering the efficiency of warehouse operations.
Data warehouse Core
This is a central repository in CRM data warehouses designed to organize sourced data in dimensional models, like star schema or snowflake schema, making queries and analysis accessible. This layer extracts data from multiple sources, stores them in a standard format, retrieves data insights, and delivers them to businesses for informed decision-making.
Presentation Layer:
By providing a single source of truth, a CRM data warehouse fosters business intelligence tools (BI tools), including Tableau, Power BI, and Looker Studio, that transform raw data into visual insights. This makes complex data analysis comparatively easy and allows teams to create reports, visualize patterns, and solve complex queries.
How to Implement Data Warehouses in CRM
Implementing CRM data warehouses is not just about technology upgrades; it’s a strategic way to make customer data usable, dependable, and insights driven.
Step 1: Define Data Sources
Identify sources that generate customer data, which typically include spreadsheets, websites, customer support systems, marketing automation tools, and CRM systems. This step precisely demonstrates where the data belongs, what type of data it is, and how often it updates so that no customer touchpoints are overlooked.
Step 2: Data Integration and Modeling
When sources are detected, develop a data model for the warehouse to store customer data to retrieve queries and analysis. This holistic approach helps businesses with an integrated system to store everything so that no data slips through the cracks.
Step 3: Choose the Right Storage
Identifying a right, tailored storage solution is an essential step in ensuring performance and scalability. Organizations often select between self-hosted or cloud-driven solutions depending on data quantity, budget, and security needs. Whichever CRM data warehouses you choose must be flexible, cost-efficient, and grow with your business.
Step 4: Structure Data for Business Applications
Raw data itself does not offer much value; it requires being transformed into something usable. When data is structured into tables, schemas, and models, it reflects actual business requirements like customer segmentation, forecasting, sales auditing, and performance monitoring. Meanwhile, well-structured data fosters prompt query response, reporting accuracy, and makes CRM integration seamless.
Step 5: Implement Advanced Analytics
The last step is transforming raw, structured data into meaningful insights. Advanced analytics, dashboards, and reporting tools help understand customer trends, performance gaps, and behavior patterns. The role of AI-powered insights and predictive analytics in data warehouses leads to improved customer experiences, fosters long-term growth, and enables smarter decision-making.
Best Practices to Set Up a Data Warehouse
- Identify your goals
- Outline the key objectives of CRM implementation, like optimizing data records, improving decision-making, and personalizing customer experience.
- Ensure your defined CRM goals align perfectly with your overall business requirements, strategies, and revenue expectations.
- Establish Data Ownership Practices
- Set up clear data administration protocols across CRM data warehouses to maintain consistency.
- Ensure quality, relevancy, and organization of data based on individual roles and priorities for integration.
- Define Data Governance Frameworks
- Outline the governance structure to ensure meeting the compliance and regulatory requirements.
- Implement clear data security and integrity policies and establish permission management practices to protect sensitive information.
- Create Change Management Processes
- Building a change management procedure helps in schema modifications and system updates.
- Continuously review the impact of modification to ensure efficient, disruption-free improvements.
- Performance Refinement:
- Partitioning: Structure tables by date or location to ensure efficient scanning of large volume queries.
- Classification: Physically arrange data according to commonly filtered columns for quick access.
- Materialized Views: This is a place where each result of executed queries is stored physically. Re-compute complex consolidations for faster retrievals.
- Query Caching: Save the frequently executed results for quick accessibility of data, query performance optimization, and effective resource utilization.
Based on the research of TDWI, businesses implementing a mature CRM data warehouse governance experience a decrease in data incident likelihood by 40% and reduce time-to-insights by 30%.
Conclusion
Data warehouses in CRM play a crucial role in optimizing customer experience for advanced businesses. The goal is to aggregate CRM data into a centralized database and deliver insights that drive clear business objectives. Whether accessing comprehensive visibility into customer relationships, enabling predictive analytics, or streamlining complex, repetitive task management.
Businesses should start strategically: begin with a demo project targeting high-impact applications, prove ROI through quantifiable results, and scale gradually. Modern technology landscape offers plenty of CRM data warehouse solutions that fit precisely across all organization sizes, from cloud solutions to enterprise-grade systems. Consider it as a strategic investment in customer relationship management that delivers actual value across sales, marketing, and support operations.









