IoT layers are the core component or the main element of IoT (Internet of Things) devices. These layers make the IoT objectives able to function that particular activity for which they have been designed. Layers of IoT make them accessible to organize the process of data collection, transmission, processing, and action between devices, networks, and applications in a structured way.
Each of these layers of IoT plays a different role in making sure that the IoT system is operating properly, effectively, and efficiently. From sensors gathering the data to delivering actionable insights and business decisions, layers of IoT are completely responsible.
Let’s move into the article and have a deep dive into the concept of layers of IoT, and the role of the IoT layers. Along with this, this blog post will aware you of the function that each IoT layer performs.
Before proceeding forward, make sure that you know what is IoT and all the basics of IoT.
What does the 7 Layers Architecture of IoT Do?
Layers of IoT perform tasks like sensing data, transmitting it securely, processing & analyzing it to make applications accessible for driving decisions & triggering actions based on insights. The layers of IoT provide a structured framework to drive the efficient functioning of IoT (Internet of Things) systems.
Furthermore, IoT layers are completely responsible for managing the data flow efficiently, maintaining system scalability, integrating diverse technologies into complied solutions, and a list of others. IoT layers divide the task into layers to simplify the design and make their development, deployment, and maintenance easier than ever.
Each layer of IoT can be scaled independently, which provides flexibility for the growth of IoT systems. IoT Layers allow you to have better control over each component for improved security and data management using different technologies and devices.
Also Read
How IoT Works: Mechanics Behind Smart Technologies
What Are the Foremost Advantages & Disadvantages of IoT?
What are the 7 layers of the Architecture of IoT ? | The Key Explanation of Each
Here, we will explain each and every layer of IoT in in-depth detail. Hence, be continue with the information, grab the knowledge, and be a pro in IoT.
1. Perception Layer (Sensing Layer)
This initial layer is basically recognized as a sensing layer but in technical terms, it is called a Perception Layer. This first layer of the IoT ecosystem consists of the physical designs of IoT such as sensors, and actuators. Along with this, this layer of IoT contains RFID tags that allow you to collect data from the real world.
Furthermore, these devices gather environmental information such as temperature sensors, humidity sensors, motion sensors, or light levels. For Instance, in a smart home, temperature sensors in the Perception Layer will collect data about the room's temperature, which can be used to adjust the thermostat accordingly.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Sensing layer:-
- The key component of the sensing layer is the Sensors that detect the Temperature, Motion, Pressure, etc
- The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags
- All the Actuators in Iot along with sensors
- Also the cameras whether they are mobile embedded and separate camera
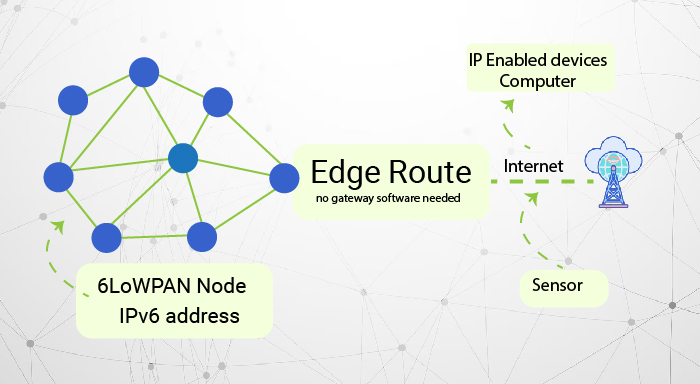
2. Network Layer (Transmission Layer)
Once data is collected in IoT devices, it needs to be transmitted to the other system for processing. The network layer comes into play and is solely responsible for this data being moved further across the different communication networks efficiently. This layer includes everything from local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs) or even the cloud.
Additionally, this layer of IoT uses various communication protocols and technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa, and 4G/5G for transmitting data securely. In the case of smart devices, the Network Layer guarantees that the collected data reaches the cloud servers, local gateways, or other devices.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Network layer:-
- All the communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and more
- The Routers and gateways
- All the cellular networks like 4G and 5G
3. Edge Layer (Processing Layer)
The Edge Layer comes into role when then the data processing task occurs closer to the source, rather than sending everything to the cloud for analysis. This layer handles the real-time processing of data to make decisions without having constant cloud communication. This IoT layer is particularly important for time-sensitive applications latency appears as an issue.
For instance, in industrial IoT, an edge layer processes the IoT sensors data from a manufacturing plant in order to detect any machinery malfunctions. It is also a response for triggering the alerts before the problem escalates.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Processing layer:-
- Edge layers contain the Edge devices such as gateways and local servers
- Local data processing is also a key component of this layer
- It holds real-time data analytics
4. IoT Data Management Layer
The IoT Data Management Layer is responsible for storing, organizing, and managing large amounts of data especially which is generated by IoT devices. This layer of IoT makes sure that the data has been collected and stored efficiently to drive easy access and analysis. Along with this, it also handles the tasks like data cleaning and aggregation.
IoT systems often deal with large-scale data using effective data management tools such as databases or cloud storage solutions. These tools are really significant for maintaining the performance and integrity of the system.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Data Management layer:-
- The cloud storage is the significant key component of this layer
- It also covers all sorts of Databases like SQLand NoSQL
- It contains all the tools that can aggregate the Data
5. Processing Layer (Analytics Layer)
The Processing Layer, sometimes referred to as the Analytics Layer to make the additional functionalities. In this layer, data is analyzed, transformed into insights, and then used to make worthy decisions.
Here big platforms like advanced analytics, and machine learning algorithms are used to identify the working patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data. For Instance, an IoT-configured farming system can use this layer to analyze the moisture levels of the soil. Later on, it forecasts the optimal time for irrigation.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Analytics layer:-
- All the platforms that have Big data such as Hadoop and Spark are the key components of this layer
- It contains all the Machine learning algorithms
- Also, the Predictive analytics is the key component of this processing layer
6. Application Layer
The Application Layer of IoT provides the user-facing interface of the IoT system by delivering specific services and solutions based on the data. It also uses analysis of the insights that have been generated by the previous layers.
This layer is responsible for making the data actionable for end-users, whether they access it through mobile apps, web dashboards, or other interfaces. For Instance, a smart thermostat of the application layer allows you to monitor and adjust your home temperature remotely just by using a smartphone app.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Application layer:-
- In the application layer, Mobile apps perform as the key component
- It has the Web dashboards
- It covers all the IoT service interfaces
7. Business Layer
The Business Layer is the topmost or the final layer in the IoT architecture that focuses on managing the overall IoT system. It involves the integration of the IoT system with the business operation, strategies, and optimization.
This layer is responsible for leveraging the data and insights from the lower layers to make informed business decisions, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. For instance, a logistics company can use IoT data for tracking deliveries in real-time, optimizing the routes, and improving customer satisfaction.
Key Components:
Here are the following key components of the Business layer:-
- The business layer requires all the Business management tools
- The Strategic planning is also the key factor here
- All the frameworks that are used to make the Decision perform as the key component here
Final Thought
IoT systems is a multi-layer architecture where it contains 7 different layers to make the functioning of the IoT layers efficient and smooth. From all the seven layers of IoT, each and every layer performs a significant role and contributes to making the IoT device accessible.
From data collection at the Perception Layer to the actionable insights at the Application Layer, every single layer plays an essential role. Using the potential of these layers of IoT, business strategies shape their future and drive success.
Hence, having an in-depth understanding of these layers will allow you to design, deploy, and optimize your IoT systems in an efficient, scalable, and impactful way. Additionally, by grasping how each layer contributes to an IoT solution, you can harness the power of your IoT technology-based business better. Therefore, let’s jump into the main content without any further ado.