Introduction
The agriculture sector has unparalleled issues to deal with ranging from water shortages to climate changes. To cope with this issue Smart Irrigation System using IoT has been developed. This technology is revolutionary and is radically changing the practice of agricultural water management.
In this blog, we’ll understand the Smart Irrigation system, its level of connecting networks, protocols, benefits, and more.
Understand Smart Irrigation System Using IoT
Modern irrigation systems involve IoT devices to regulate the amount of water supplied through analytics and automation. Unlike other measures that can be fixed, these systems have a way of adjusting to a given environment so that water is distributed well. To better grasp their worth, one has to dive deep into the levels of IoT and the corresponding communication that permits them.
IoT Levels In Smart Irrigation
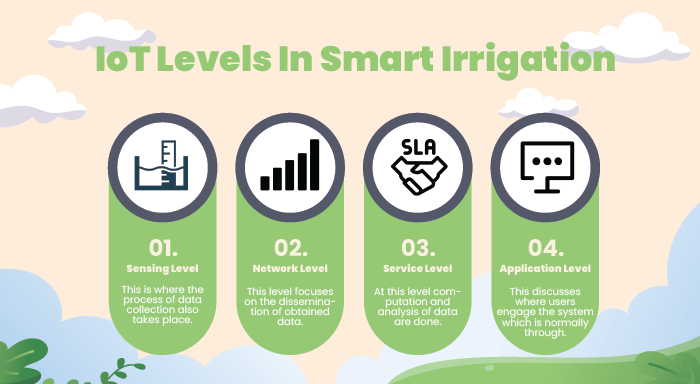
IoT systems typically operate across four main levels:
1. Sensing Level:
This is where the process of data collection also takes place. In smart irrigation, this IoT level comprises soil moisture sensors, weather, and other environmental sensors.
2. Network Level:
This level focuses on the dissemination of obtained data. That is where different protocols start to kick into play.
3. Service Level:
At this level computation and analysis of data are done. Control verticals of the cloud platforms and edge computing devices take place here to process the collected information.
Also Read
IoT Control Panel | Seamless Management for All Your Smart Devices
Internet of Things | IoT Design Methodology And Its Importance
4. Application Level:
This discusses where users engage the system which is normally through smartphones or web applications for the regulation of irrigation systems.
Communication Protocols in IoT for Smart Irrigation
Communication Protocols in IoT are most important for the interconnectivity between the number and types of devices so they could share data at the best speeds. Some key protocols used in smart irrigation systems include:
1. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport):
Made for low-bandwidth, high-latency situations, MQTT is a great fit for distant agricultural applications.
2. CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol):
Popular among low-power devices and is well-suited for sensors that work with the smallest of power.
3. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network):
This protocol enables communication over a large distance consuming minimal power and hence can be useful for large farms.
4. Zigbee:
A short-range, low-power protocol is often used for creating mesh networks of sensors in a field.
5. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT):
This cellular technology is gaining traction because it provides wide-area coverage with low power requirements.
Functional Blocks Of IoT–Based Smart Irrigation Systems
Understanding the functional blocks of IoT based smart irrigation systems helps illustrate how IoT levels and communication protocols work together:
1. Soil Moisture Sensors:
Existing at the sensing level, these devices estimate the amount of water in the soil a concept important to the irrigation process.
2. Weather Stations:
They also acquire sensing data concerning temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed at the sensing level.
3. Microcontrollers:
Such devices are those such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi, which work on the service level, performing the data processing and the management of the actuating devices.
4. Actuators:
Applications of smart valves and pumps entertain the water flow depending on decisions made at the service level.
5. Wireless Gateways:
These devices are network-level devices that help in the connection of sensors to the cloud platform through one or the other protocol.
6. Cloud Platform:
It is a service-level component that holds and processes data, the use of machine learning for making decisions is sometimes added.
7. User Interface:
At this level, farmers use applications on their smartphones or through an internet site to engage in the application.
Advantages of Smart Irrigation System using IoT
The smart irrigation system using IoT yields numerous benefits:
1. Water Conservation
These systems dispense water in the quantities and at the time when they are most required and hence may minimize water use by half of what the conventional approaches demand.
2. Betterity and quality of crops
The accurate management of water results in healthier plants and better production of crops; in fact, the yields may improve by 20-30%.
3. Cost Savings
Smart irrigation systems are slightly more expensive than traditional systems in the initial setup; however, they prove more efficient by minimizing human resources and expenses in the long term.
4. Energy Efficiency
Proper control in the pumps and enhanced water management decrease energy use resulting in lower expenses and inch towards eco-friendliness.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
The availability of real-time and historical data lets farmers make rational decisions concerning irrigation and other work at the farms.
6. Environmental Impact
Hence, by the efficient use of water, these systems help advance the conservation of resources used in farming practices.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
Due to the flexibility of the IoT levels and communication protocols, IoT-based systems are easy to scale and apply to different farm sizes and crop types.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite their benefits, smart irrigation systems face challenges:
1. Initial Costs:
The cost may include hardware, which is sensors and actuators in IoT, and networking equipment which can be expensive initially.
2. Technical Complexity:
To carry out these systems, there is a need to note the levels and communication in an IoT system.
3. Connectivity Issues:
In remote areas internet connection is difficult and this may lead to poor internet connection which may slow down the system.
4. Data Security:
Unfortunately, like in any IoT system, there are issues such as data privacy and security.
However, the future of smart irrigation looks promising:
- Advanced AI Integration:
Additional improvements in the predictability of the results and effectiveness of the system through complex AI means.
- Improved Sensor Technology:
Design and realization of higher accuracy, longer life-span, and lower cost IoT sensors.
- Standardization of IoT Protocols:
The development of norms of the IoT in agriculture contributes to better integration of the devices and lowering of the costs that present themselves with this implementation.
- 5G Integration:
With the advent of the 5G networks, there will be improved, and efficient connectivity of the IoT devices in the agricultural context.
Conclusion
Smart irrigation systems using IoT levels and communication protocols represent a significant leap forward in agricultural water management. By combining real-time data collection, automated decision-making, and precise control, these systems offer a solution that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment.
As we face the dual challenges of feeding a growing global population and managing increasingly scarce water resources, the role of IoT-powered smart irrigation in sustainable agriculture cannot be overstated. It's not just about saving water; it's about reimagining our relationship with this vital resource and paving the way for a more sustainable and productive agricultural future.
Also Check
Unveiling the Essential Building Blocks of IoT
Learn the Ideas Behind the Logical and Physical Designs of IOT
Access Control of IoT Devices: Ensuring Security & Efficiency
Role of Advanced Technology in attaining Sustainable Farming