Cities, whether they are big or small, are becoming intensely populated due to the rise of urbanization. To effectively handle sanitation, traffic congestion, healthcare, environmental degradation, and rising energy consumption, cities are looking to adopt modern technologies to improve their city plan. One of the cutting-edge technologies that streamlines cities and make them more efficient is the Internet of Things. Executing IoT-driven smart city solutions is making sure that urban life becomes safer and more convenient. It is while allowing cities to enhance public utility services and infrastructure. In this article, we will study the capabilities of IoT technology with practical IoT smart city examples, possible advantages, and more. So, let’s get right into it-
What Is IoT?
IoT, short for Internet of Things, can be defined as an expansive network of physical objects ranging from home automation devices such as Amazon Alexa or smart watches to large-scale industrial machines. Such devices are often embedded with software, sensors, and connectivity. Their job is to collect information from an environment and exchange data to perform a specific task. All of this happens without considerable human interference, creating “smart environments” and ensuring total automation and new insights.
IoT in Smart Cities: Real World Applications
In recent times, there has been an increased focus on IoT smart cities as diverse countries around the world are adopting it. Basically, IoT helps enhance efficiency, minimize costs, and improve quality of life for the residents. It leverages IoT-enabled devices like RFID tags, Bluetooth sensors, actuators, and meters to collect data in real-time for future analysis. Leveraging this data, the municipalities can enhance services, infrastructure, public utilities, and more.
Some of the real-world IoT smart city examples are as follows:
Smart Traffic Management:
You can install IoT sensors on roadways, traffic lights, and vehicles to collect data on various indicators like congestion, traffic patterns, and accidents. This data can be utilized to streamline traffic flow, minimize congestion, and enhance road safety. Such solutions leverage GPS data and sensors to collect information from the driver’s smartphone and tell the exact speed and location of the vehicle. Moreover, utilizing this historical data allows you to forecast the preferred routes and avoid possible congestion problems.
Real-life Examples:
- New York: Testing a project of connected vehicles (CTV) to remove accidents related to traffic, damage to property and life, and mitigate injuries.
- Los Angeles: It has implemented road-surface sensors and CCTV to control the flow of traffic with real-time data. The city has also implemented smart controllers that adjust lights automatically as per the evolving traffic conditions.
Intelligent Parking:
In parking spaces, IoT sensors can be installed to detect when a particular spot gets occupied and transmit the information to a central server. This can help drivers find relevant spots in the parking lot, minimize congestion, and search time. The sensors active on the group send the data to the cloud, notifying the driver instantly whenever a parking spot becomes empty.
Real-life Examples:
London (UK): The SmartPark project implemented in Westminster enables drivers to locate parking spots on the go. It removes the hassle of time-taking searches for an empty spot and reduces congestion.
Public Safety:
IoT-enabled sensors and cameras can be embedded in public spaces to track possible security threats, like unintended bags or suspicious activities. IoT-driven solutions come enhanced with real-time tracking, analytics, and decision-making capabilities. Assessing the data generated from acousting sensors and CCTV cameras installed across the city and also the data extracted from social media feeds aids in forecasting possible crime incidents. This can assist law enforcement agencies react quickly and effectively to threats.
Note: To learn how IoT cameras can enhance workplace security, you can check out our dedicated blog.
New York (USA): The New York City fire department utilizes data modeling and predictive analytics to recognize crime hot spots. The city has also implemented a gunshot detection solution that utilizes connected microphones to transmit information to cloud platforms. This platform basically calculates the time taken by the gunshot sound to reach the microscope and figure out the exact location of the gun to notify the police on a mobile app.
Waste Management:
Waste collection operators leverage IoT-enabled solutions to streamline collection schedules and routes. An efficient IoT system can track fuel consumption, waste levels, and waste containers use in real-time. IoT sensors can be installed in garbage cans and recycling bins to track the fill level and streamline the waste collection routes, minimizing costs and environmental impact. Every container will have a sensor installed on them that detects waste levels. Once a container closes in on the threshold levels, the truck driver gets an immediate notification on a mobile to empty a complete container and prevent emptying it when it is half-full.
Real-life Example:
New Jersey (USA): The East Brunswick municipality has released a recycling allowed with IoT capabilities. It aids in enhancing their overall communication with the residents to enhance recycling rates and minimize waste.
Utility Management:
IoT-powered smart solutions allow citizens to save a considerable amount of money on home utilities with:
Energy Management: IoT sensors can be installed in homes and buildings to track energy usage and streamline energy consumption, minimizing carbon emissions as well as costs.
Intelligent Lightning: City planners can ensure that all the streetlights have IoT light sensors installed on them to adjust the lightning level as per the ambient light, minimizing pollution and energy consumption.
Water Management: IoT devices can also be connected with water distribution systems to track water quality, detect leaks, and streamline water utilization, conserving resources and minimizing costs.
Remote Monitoring:
IoT-driven solutions allow municipalities to track environmental conditions remotely. For example, sensors can be installed to water grids to inspect the quality and ensure notifications in case of leakages or changes in water chemical composition. The same technology is also utilized for tracking air quality in locations that are prone to pollutants and suggests solutions that can greatly boost air quality.
We have a dedicated blog on Remote Control in IoT which you can go through to understand what it is and how it is revolutionizing logistics and supply chains.
Real-life Example:
Copenhagen (Denmark): It has tremendously improved the green standard by implementing smart grids to minimize carbon emissions from heating platforms. This project provides new energy infrastructure that supports all energy forms, including efficient buildings, electric transport, and HVAC platforms at full scale.
Public Transport:
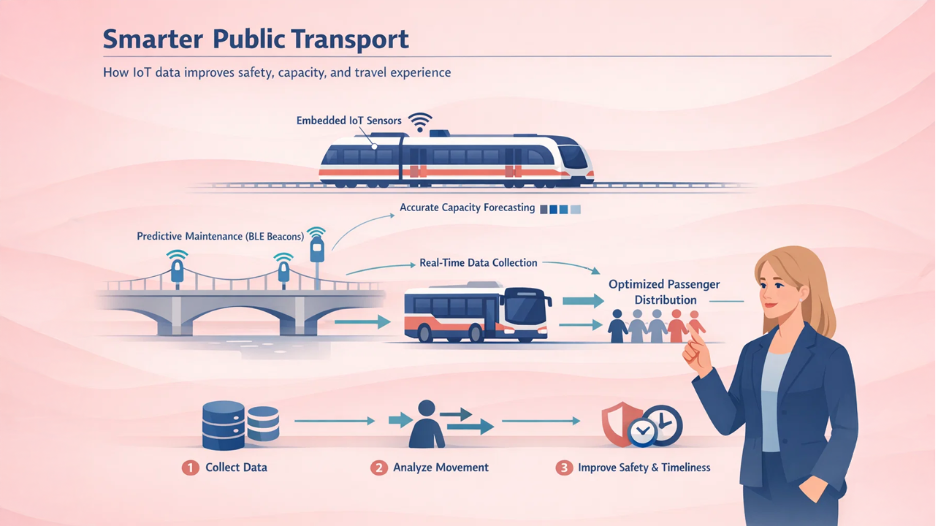
Traffic operators can utilize the data from embedded sensors in numerous sensors to assess and recognize patterns of utilizing public transport. This data aids in achieving a standardized level of timeliness and safety while minimizing wait times and improving travel experience of citizens. A smart city can also have something called BLE beacons on bridges and roads to track wear and tear and repair them instantly in case of expected damage.
Real-life Example:
London: Train operators can leverage IoT technology to forecast the train passenger cars accurately on their journey in and out of the city. They centralize the data from sensors, CCTV cameras, and ticket sales to have an accurate forecast of the exact number of passengers that the car will load. When a train arrives at the station, operators can suggest passengers disperse across the train for optimal use of capacity and uniform loading.
Overall, IoT technology is a key technology that enhances the efficiency and sustainability of smart cities, making them more convenient, enjoyable, and livable for people.
What Are the Advantages of IoT in Smart City Implementation?
The advantages of IoT are several and far-reaching. IoT facilitates efficient use of connected systems, apps, devices, industrial appliances, buildings, streets, and more to create optimal working and living conditions. The key benefits of IoT with respect to smart city implementation are as follows:
- Enhanced Infrastructure Management: IoT technology can be utilized to track and handle the vast infrastructure of the city, including roads, bridges, and buildings. This can help recognize maintenance requirements, minimize downtime, and enhance overall safety.
- Improved Public Safety: IoT-powered cameras and sensors can aid in enhancing public safety by detecting possible security threats, monitoring criminal activity, and tracking emergency response times.
- Effective Transportation: IoT aids in streamlining public transportation routes, minimize congestion, and enhance traffic flow. Connected vehicles can also interact with one another and with traffic platforms, allowing safer and more effective travel.
- Energy Efficiency: IoT technology allows tracking and management of energy use in public spaces and buildings, minimizing energy waste and saving costs.
- Enhanced Waste Management: IoT sensors collect data related to waste management and can help in finding the best routes, minimizing the impact of garbage collection and reducing costs.
- Improve City Engagement: IoT-powered platforms can allow citizens to do their bit in city planning, and ensure feedback on urban services, and report real-time issues.
- Wellness and Health: IoT can be used to track air quality, detect environmental problems, and monitor health trends. This ensures crucial feedback for public health officials to create policies that enhance the health of the citizens.
Conclusion
IoT smart city initiatives are changing the urban environments by connecting services, infrastructure, and citizens through real-time information. From traffic management as well as public safety to energy, waste, and environmental tracking, IoT-enabled technologies allows cities to work with higher sustainability, efficiency, and resilience. Such solutions minimize operational expenses, improve quality of life, and support data-driven decision making for city planners. As urban populations start to rise across the world, IoT smart city frameworks will play a key role in developing greener, safer, and more responsive cities specialized to align with future demands.