Introduction
Wired and wireless communication has been completely reinvented through the IoT causing a need for Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs). One invention that can be recommended to be put to use to meet these needs is LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network). Being one of the protocols in communication protocols in IoT, for a low-power wide area network, LoRaWAN has reliable communication and power channels, low power usage, and coverage area over large distances.
This article provides insights and analyses on how LoRaWAN works, where it can be used, and where it is headed.
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a protocol for communication to low-power, nonpublic networks for regional national, or international coverage. It is a product of LoRa Alliance and adopts the LoRa modulation that guarantees long-haul connectivity in a low-power regime. This combination makes it suitable for those devices that transmit analogous data to other devices occasionally, over large expanses of the network.
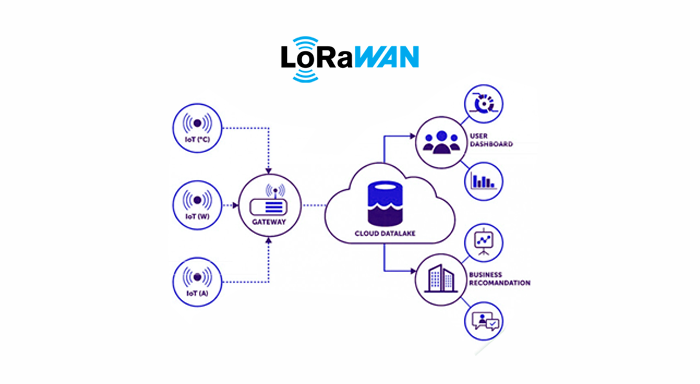
How Does LoRaWAN Work?
LoRaWAN is based in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) radio bands that are free of charge worldwide but vary by area, such as 868MH in Europe, and 915 MH in North America.
Key Components of LoRaWAN:
1. End Devices:
These are the sites or points through which data is gathered and transferred to other points. They are designed for minimum power consumption to make them run for longer on batteries hence are most suitable for use as handheld tools.
2. Gateways:
They are intermediate devices that connect end devices to the network server. They get RF data packets from end devices and transfer them to the network server through backhaul like Ethernet cables, cellular, and WiFi.
3. Network Server:
It governs the network and oversees the accuracy of the data as well as the security of the network at IoT levels. The server also plays a role in determining the flow of data, over the network depending on the signal strength from the gateway as well as the load it has to handle.
4. Application Server:
In turn, this server analyzes and uses the data that end devices transmit, ITU.
× It is the core of data analysis and setting up the foundation for practical application of the analyzed information.
Advantages of LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN's unique combination of range, battery life, cost, and built-in security features offers several advantages:
1. Long Range:
LoRaWAN hardware can cover more than 10 Km in rural areas and 15 Km in urban areas.
2. Low Power Consumption:
Low power consumption is one more advantage of LoRaWAN: end devices can work over the battery for years.
3. Security:
LoRaWAN ensures secure communication via two layers of security: it will create one for the network and one for the application. This two-layered security helps to prevent tampering with the data, and even listening into the data stream.
4. Scalability:
Because of the star structure, LoRaWAN is said to be able to handle virtually an unlimited number of devices, perfect for large-scale applications like smart cities or industrial IoT.
5. Cost Efficiency:
The decision to employ ‘unlicensed bands reduces devoting substantial finances to spectrum licenses hence lowering operational costs.
Applications of LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN is versatile, catering to a broad range of applications across various industries:
1. Smart Cities:
The key use cases of a smart city utilizing LoRaWAN are smart street lighting, waste management, air quality, and energy management. For instance, smart meters can enable the transfer of information to utility firms to improve the use of energy and lower costs.
2. Agriculture:
In agriculture, LoRaWAN can control soil moisture, weather conditions as well as crop health and is essential input that the farmers need when irrigating the crops.
3. Industrial IoT:
The use cases in the industry include equipment monitoring, condition-based monitoring, and asset tracking. Thus, through collecting real-time data, companies can improve many aspects to provide better service and avoid time losses.
4. Healthcare:
LoRaWAN is useful in the healthcare segment. Patients’ status can be closely monitored without frequent hospital visits, which is useful when attending to individuals with chronic illnesses and the elderly.
5. Logistics and Supply Chain:
It is useful in supply chain management through tracking the location of assets and inventory to make the supply chain efficient. Such components integrated with the shipping containers or pallets can monitor the location and condition of the goods in real-time.
Future Prospects of LoRaWAN:
5G Integration:
LoRaWAN can coexist with 5G networks since it targets the ‘anytime, anyplace, anywhere’ connectivity of nonJam 5G but for relatively low bandwidth IoT devices that do not require high data rates.
Enhanced Security:
When the use of IoT increases, measures will have to be improved to ensure the security of IoT devices. In future updates of LoRaWAN, there are rumors of improved encryption and authentication frameworks.
Global Adoption:
Continues by the LoRa Alliance and developments by many industries ensure that the world embraces technology. Broad adoption will also be driven by efforts to interconnect LoRaWAN with other types of IoT standards.
Conclusion
LoRaWAN is a groundbreaking technology that addresses the key challenges of IoT communication: specifically, they are high member distance, low output power, and low production cost. Thus one can conclude that its possible uses extend across industries demonstrating its diverse possibilities.
However, the solutions are beneficial, and future trends in technology for LoRaWAN are optimal for enhancing global IoT prospects and collaboration with different industries.
By focusing on interoperability, security, and integration with emerging technologies, LoRaWAN will continue to be a pivotal player in the IoT ecosystem, driving innovation and connectivity in ways previously unimagined.