In the last few years, advanced technological landscapes have introduced numerous technologies, transforming industries, homes, transportation, and offices. The Internet of Things (IoT) stands out among the innovative technologies that have revolutionized how humans work and interact with surroundings. It facilitates modern integration between devices with the focus on the creation of smart solutions across industries and geographical regions. However, any developer aiming to establish a career path in this field must cultivate a broad spectrum of skill sets. Additionally, the market value is also experiencing unprecedented growth and is expected to cross $630 billion in 2026 based on the latest data insights. As the IoT realm is evolving rapidly, it engages millions of developers around the globe. With growing IoT solutions all around the world, the IoT market is expected to grow even further.
Understanding the basics and key concepts deeply is essential for developers aspiring to a successful career in IoT. If you are someone who wants to learn these concepts precisely, you can consider IoT interview questions, where each topic is comprehensively covered, like the logical and physical design of IoT. Having detailed knowledge of these frameworks enables IoT developers to comprehend effective deployment.
This blog offers you a comprehensive overview of the logical design of IoT, as well as the physical design of IoT, and explores the impact of their synergy. It will also highlight the core components and their compatibility that help develop reliable, effective, and scalable IoT solutions.
However, before proceeding ahead, first understand what IoT actually is and how it impacts our daily lives
What Is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to an interconnected network of physical devices embedded with sensors or actuators. This robust network allows devices to collect, process, and share real-time data. It is widely used in various industrial applications like smart homes, smartwatches, transport, and industrial applications. With IoT, these devices can communicate and exchange data with each other and across internet-enabled devices. This accelerates the adoption of IoT across industries globally.
The industries include:
Healthcare- Remote patient monitoring and real-time health data analytics to foster personalized care.
Weather monitoring systems in IoT- Gather, analyze, and transmit atmospheric data to predict weather patterns and detect unusual activities.
Manufacturing- Managing, controlling, and automating machines in industrial firms to enhance efficiency, predictive maintenance, and boost productivity.
Agriculture- Check soil health, track environmental conditions, and streamline crop management to enable precision farming.
Fundamentals of Logical and Physical Design of IoT
Even if you are just starting to explore the world of IoT, you must use smart devices like your smartphone, fitness tracker, automated alarm, and biometric systems in your offices. All these devices are nothing but a real-life implementation of a valuable term, IoT, Internet of Things. But the question is, what makes these devices smart enough? Maybe the basic design architecture of IoT.
And IoT environments mainly classify their design architecture into two crucial types:
- Physical Design of IoT
- Logical Design of IoT
Let us deep dive into the detailed explanation of these design architectures with this comprehensive guide.
Logical Design: The IoT’s Brain
Think of IoT as a single element instead of a collection of interconnected physical devices. Logical design acts as the brain of a complete IoT ecosystem. Basically, it comprises the flow of data and how they exchange, process, and store data. The logical design of IoT empowers IoT developers to assess protocols, data models, and different rules that describe the workflow of IoT platforms.
Physical Design: The IoT’s Body
Hope you get familiar with logical design; now the IoT ecosystem also needs a tangible body for effective functioning. The body of IoT is outlined by the physical design that embeds sensors, microcontrollers, and network infrastructure, allowing you to collect and share data in the real world. These physical designs of IoT involve devices that you can actually touch, observe, and interact with in your surroundings. The role of these designs is to execute IoT capabilities in the physical world.
However, having knowledge of both the logical and physical design of IoT is important because they are connected with each other and interoperate. No matter how advanced your sensors are, they will only function correctly in an IoT environment if you have implemented the correct data protocols. On the other hand, a reliable software architecture needs strong hardware for effective deployment.
In the succeeding sections, let us understand both components of the design architecture:
Physical Design of IoT
The physical design of IoT contains several physical devices integrated with an IoT environment, and the protocols utilized to ensure a real-time IoT ecosystem. Every IoT device is responsible for specific tasks such as remote sensing, actuating, etc., depending on the environment they are actually connected to. These devices can also move data and share files using different types of wired or wireless connections. For efficient performance evaluation and workflows for improving the system, these architectures are used to create data.
There are two key components of IoT physical design: IoT node devices and IoT communication protocols. Let’s discuss them briefly:
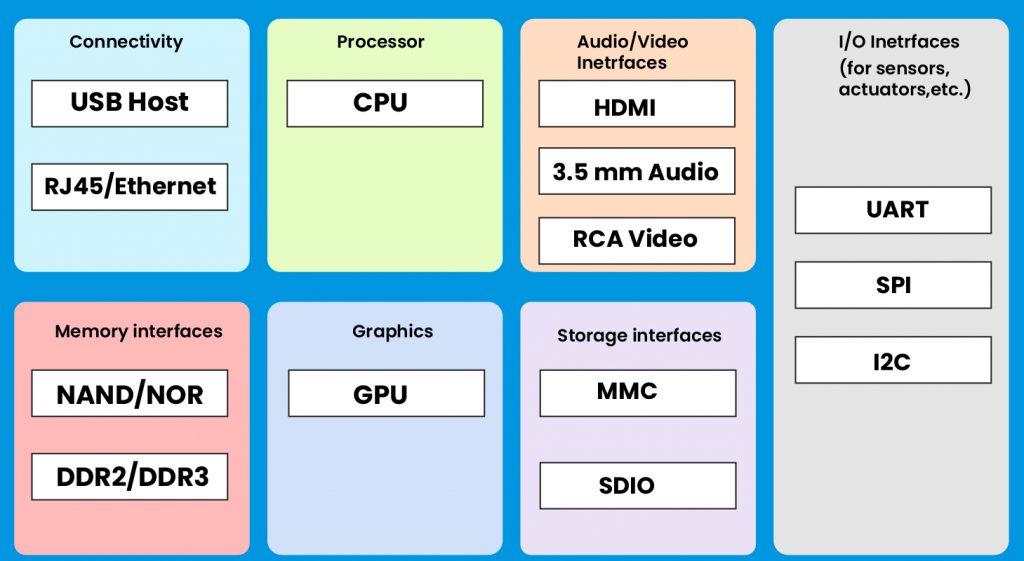
Node Devices
Node devices are leveraged to develop connections, process data, display interfaces, and log data in an IoT environment. Node devices generate sensor data that the IoT environment can analyze and are programmed to deploy processes and optimize the system.
Now, from the following points, let us try to comprehend which devices are suitable for which use cases.
- Audio/Video Interfaces: System interfaces, like RCA and HDMI devices, are used to record videos and audio.
- Network Access: Devices like Ethernet ports and USB hosts foster connectivity between the server and devices.
- Processor: The central processing unit and other units analyze the information. This is used to improve the decision-making ability of an IoT environment.
- Input/Output: Devices including SPI, CAN, UART, etc., deliver input and output indicators to IoT sensors and IoT actuators.
- Activity Control: GPU and DDR devices manage the IoT system activity.
- Storage Interfaces: IoT devices such as SD, MMC, and SDIO are utilized for storage of data.
IoT Protocols
IoT communication protocols help in establishing a connection between the node device as well as the server via the internet. Essentially, it sends commands to an IoT device and then receives data from the IoT device. Both client and server side depend on distinct types of protocol. Furthermore, these IoT communication protocols are managed via network layers. The main types of network layers include transport, application, network, and link layers. IoT communication protocols are one of the pillars of logical and physical design of IoT.
Some of the protocols are
- HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)- This protocol is utilized for transmitting media documents by establishing a communication link between servers and web browsers.
- Application Layer Protocol: Protocols used in this layer define how the information is being sent over the network. It depends on underlying link, transport, and network layer protocols to deliver the information across the network. Examples of Application layer protocol includes: WebSocket, MQTT, XMPP, AMQP, and DDS protocols.
- Web Socket: It allows two-way communication between the host and the client and mostly web browsers leverage it.
- Transport Layer: It controls the overall flow of data segments. Moreover, it also manages error-control and end-to-end capability for message transfer.
- Transmission Control Protocol: It sets up and maintains a network that can ensure data exchange via the internet protocol.
Different types of network layer are as follows-
- Network Layer: In IoT, the network layer is basically used to send datagrams from the source network to destination network. Main examples of network layer include IPv6 and IPv4.
- Link Layer: The link layer is utilized to send data over the physical layer of the network. It defines how the packets are being programmed and signaled by the devices.
- Ethernet: It is a comprehensive set of protocols utilized in Local Area Networks that defines the medium access control and physical layer of LANs.
- Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi): It is a group of LAN protocols. It defines the set of media access controls and physical layer for LANs.
Logical Design of IoT
It is the actual design of the IoT system. It illustrates the assembling and configuration of the components i.e. computers, sensors, and actuators.
As stated earlier, logical design describes the brain of the IoT system. It describes the configuration and assembling of components, which includes sensors, computers, and actuators.
The various components of IoT Logical Design are as follows:
- IoT functional blocks.
- IoT communication models.
- IoT communication APIs.
- Web-Socket-based Communication API
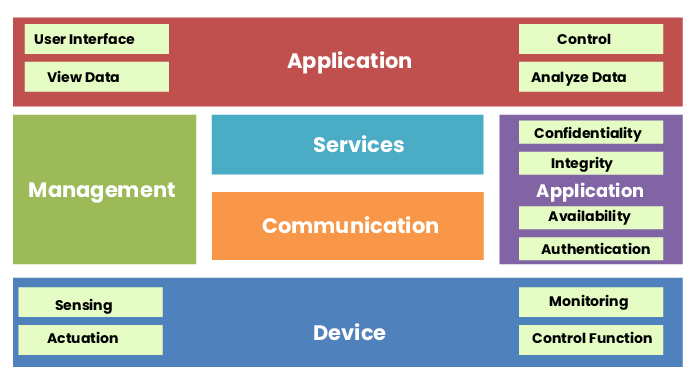
1. IoT functional blocks
The IoT functional blocks support diverse capabilities, like identification, sensing, management, actuation, and communication. Functional block offers a few devices to control interaction between host and server. This facilitates monitoring of control functions, managing data transfer, safeguarding the IoT system through authentication, and providing an interface for monitoring and controlling several functions. IoT functional blocks are one of the most important factors in the logical design of IoT.
The functional blocks of IoT include the following:
- Device: Devices render actuation, sensing, tracking, and control functions to the IoT platform. The common devices used in the IoT ecosystem include the following sensors, RFID tags, appliances, actuators, machines, and gadgets. These devices can be tethered to the IoT environment either via wireless chip or cable.
- Communication: It handles communication within the IoT environment. Communication is a crucial facet of the entire IoT framework as this makes IoT devices capable of communicating with another platform or with one another.
- Services: Services cover various functionalities like device control, device tracking, device discovery, and data publishing. In Internet of Things, there is a management service layer which is responsible for handling these services.
- Management: This functional block provides functionalities to control the IoT system. It includes numerous functions such as controlling and handling the devices, enforcing standards of security, implementing data encryption and segmentation, etc.
- Security: It ensures security for the IoT platform. It performs authorization, authentication, data security functions, and message and content integrity. Security helps in safeguarding devices and save details from manipulation, theft, and unauthorized accessibility.
- Application: The application functional block provides an interface where users can track and control numerous facets of the IoT system. It empowers users to check the status of the system and assess the processed data. The user-friendly interface helps users to ensure effective use of the collected data.
2. IoT Communication Models
The goal of IoT communication models is to promote robust interaction between the server and the system. The different types of IoT communication models offer the following models:
Request-Response Model:
This model efficiently transfers client request signals to the server, and then the server responds to the request. As the server receives the request, it decides how to respond by re-accessing the data, connecting the resource representation, generating the response, and delivering responses to the client. In this model, HTTP is the only protocol followed between server and client.
Publish-Subscribe Model:
The model contains three crucial components: Brokers, Publishers, and Consumers.
- Publisher: It is the data source that transfers data to the topic.
- Consumers: In the publisher-subscribe model, the consumer subscribes to various topics.
- Brokers: The brokers then accept the data sent by the publishers and send it to the consumers.
Push-Pull Model:
The model comprises of data consumers, data publishers, and data queues:
- Publishers: In the push-pull model, the message is first published by the publishers and then pushed in the queue.
- Consumers: Consumers remain present on the other side and get the data out of the queue.
- Queue: It aids in decoupling the message between consumer and producer.
Exclusive Pair:
Exclusive pair forms the bi-directional model that involves full-duplex communication between the server and client. In this model, the client first sends the request, and the server stores the record of all the connections. Here, only the WebSocket-based communication API is utilized.
IoT Communication API:
There are two distinct types of communication API:
REST-driven Communication API:
The full form of REST is Representation State Transfer. It involves a complete set of architectural protocols via which you can design web APIs and web services. Such APIs and web services focus on the resources of the system and how the resource states are being sent and addressed. It depends on a request-response communication model, and the architectural aspects include connectors, components, and data elements. They collaborate via a distributed hypermedia system.
The main benefits of REST-based communication APIs involve the following:
Flexibility: REST APIs support a diverse range of applications and services. They can provide support to straightforward web apps to a more complete enterprise platform.
Simplicity: The process to design and deploy REST API does not involve any complications. This is precisely the reason why it has emerged as a preferable choice for creating APIs for web applications.
Stateless: Every request in REST API is independently processed and is not associated with previous requests. This simplifies distribution and scalability.
Caching: REST APIs depend a lot on caching to improve performance and reduce service load.
Web-Socket-driven Communication API:
Web-Socket API can be described as the full-duplex and bi-directional communication model between servers and clients. It does not need a fresh connection to set up for every message between servers and clients. Once the connection is established, the messages can be consistently sent and received without disruption. It is an ideal choice for IoT applications with specific needs such as high throughput and low latency.
Go through the following points to understand the benefits of web-socket-based communication APIs:
- Scalability: Since they can render support to a vast range of connections (up to thousands) per each server, Web Socket APIs prove to be extremely scalable.
- Efficiency: Web Socket APIs prove to be more efficient in real-time communication. They depend on consistent communication to ascertain bidirectional communication.
- Reduced Overhead: When compared to Rest APIs, it has comparatively less overhead since it relies on single-point communication to transfer information.
- Real-time Communication: Web Socket APIs are the best option for applications that rely on real-time updates. They are more widely preferred because they allow strong communication between client and server in real-time.
Fog and Edge Computing in IoT Architectures
As IoT networks start to become more layered and decentralized, extensively relying on cloud infrastructure can cause performance issues. To fix this problem, edge and fog computing are vastly integrated in IoT logical design.
As far as edge computing is concerned, the information is processed locally either via gateways or routers or within the device. This proves to be crucial for latency-sensitive application areas such as autonomous vehicles, smart cameras, or predictive maintenance in factories. Fog computing ensures intermediate processing between remote cloud infrastructure as well as local edge nodes, allowing real-time analytics and bandwidth optimization.
When edge and fog computing are combined, they improve scalability, efficiency, and responsiveness of IoT deployments while proving to be compatible with distributed and modular architecture.
Security and Privacy in IoT Design
With the increasing number of integrated platforms, representing privacy and security has become a crucial element of IoT physical design. This is why effective protection is more crucial than ever; as IoT connectivity increases the risk of data breaches, illegitimate access, and unauthorized changes at the device level.
From physical enclosures and secure boot functionality to end-to-end encryption and access management, every layer requires robust protection. Protocols that are necessary for network encryption ensure its security, while application-level controls such as token-based authentication and Application Programming Interfaces safeguard user control.
Privacy issues also need strategic solutions. A few specific strategies, like data masking, data minimization, and compliance adherence with GDPR/CCPA guidelines, ensure that the personal data is managed responsibly. Integrating zero-trust models for reliable hardware components and privacy into physical design streamlines the creation of flexible and fault-tolerant IoT ecosystems.
Comparing Logical Designs of IoT and Physical Designs of IoT
The following table expound on the main difference between logical and physical design of IoT:
| Aspect | Physical Design of IoT | Logical Design of IoT |
| Definition | Comprises the tangible devices and components utilized in the IoT platform. | It involves the abstract system describing the functionality of an IoT system as well as the data flow. |
| Focus | Hardware elements such as actuators, sensors, devices, network infrastructure, and communication modules. | Interaction models, software architecture, data processing, and communication protocols. |
| Components | Includes gateways, IoT devices, cloud servers, RFID tags, physical network setups, and cloud servers. | Involves message queues, APIs, event-based logic, data formats (XML, JSON), and services. |
| Representation | Covers the type of devices that exist and their placement in the network. | It deals with how devices process, communicate, and share data. |
| Example | One of the common examples is a Wi-Fi module sending information to the cloud. | The logical design covers transmission of data through MQTT protocol and assessed via stream-processing service. |
Final Verdict
The IoT, the Internet of Things, is one of the important pillars that transforms the modern technological solutions that we see today. A few of the crucial examples of IoT include automated cars, smart gadgets, intelligent agriculture machines, healthcare monitors, etc. The importance of IoT lies behind their niches, industries, and geographical regions. It is highly useful in weather tracking systems, healthcare platforms, and smart cities. Although, creating an effective and intelligent IoT ecosystem is essential for IoT developers to gain proficiency in their technical skills.
This blog has uncovered all the fundamental concepts of logical design of IoT, as well as physical designs of IoT. Both the logical and physical design of IoT are becoming the foundation for creating a successful IoT system. Physical designs of IoT manage the infrastructure of the IoT system, while logical design highlights intelligence and communication models.
Physical designs are all about real-time components that you can touch and see, such as sensors or actuators, as well as communication models. In contrast, the logical designs concentrate on functional blocks, APIs, and messaging protocols. To foster success in every IoT development project, it is essential to understand how physical and logical design function and their interoperability.
Related Posts
Internet of Things | IoT Design Methodology And Its Importance
Unveiling the Essential Building Blocks of IoT
IoT Data Visualization | Understand the Power of Connected IoT Devices