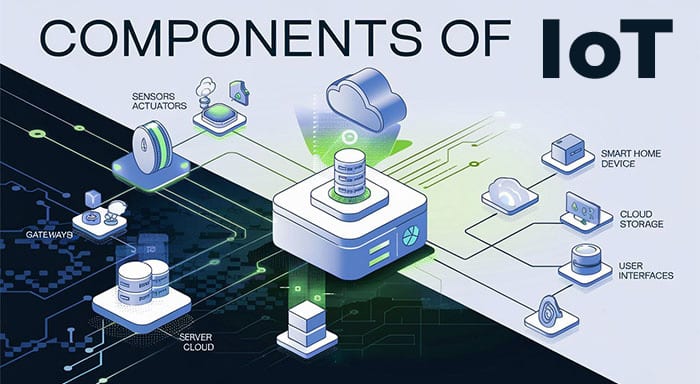
The Internet of Things is a modern technology that tethers various systems, devices, and software in an IoT ecosystem to gather and exchange data. This interconnectivity ensures automation, efficient collection and exchange of data, intelligent decision-making, and enhanced efficiency across the industry. To understand the fundamental blocks and conceptual framework of IoT, it is important to understand the components of IoT that make such systems functional.. Each of the components mentioned in the blog plays an instrumental role in determining feasibility and success of IoT solutions. So, let us discuss major components of IoT in this blog-
Let us cover a few basics first before proceeding ahead.
What Is IoT?
Before diving deeper into the components of IoT, let’s cover some IoT basics to establish the context. IoT has emerged as one of the most significant technologies for businesses in the modern world. We connect diverse systems such as thermostats, kitchen appliances, baby monitors, and even cars to the internet. Through these systems embedded with IoT actuators and sensors, smooth communication becomes possible between devices, processes, and people.
IoT also leverages cloud technology, cost-effective computing, big data concepts, mobile technologies, and analytics. It makes the process of data collection, storage, and analysis a lot streamlined, requiring little to no human intervention. IoT has made our world hyperconnected where multiple digital systems are connected with each other regardless of location.
Key Components of IoT Infrastructure
The working of IoT revolves around collecting information in the environment, storing the data in the cloud, using software to process the data, and giving output to the user. The operation of IoT is facilitated through the following key components of IoT:
1. Sensors: One of the core components of IOT
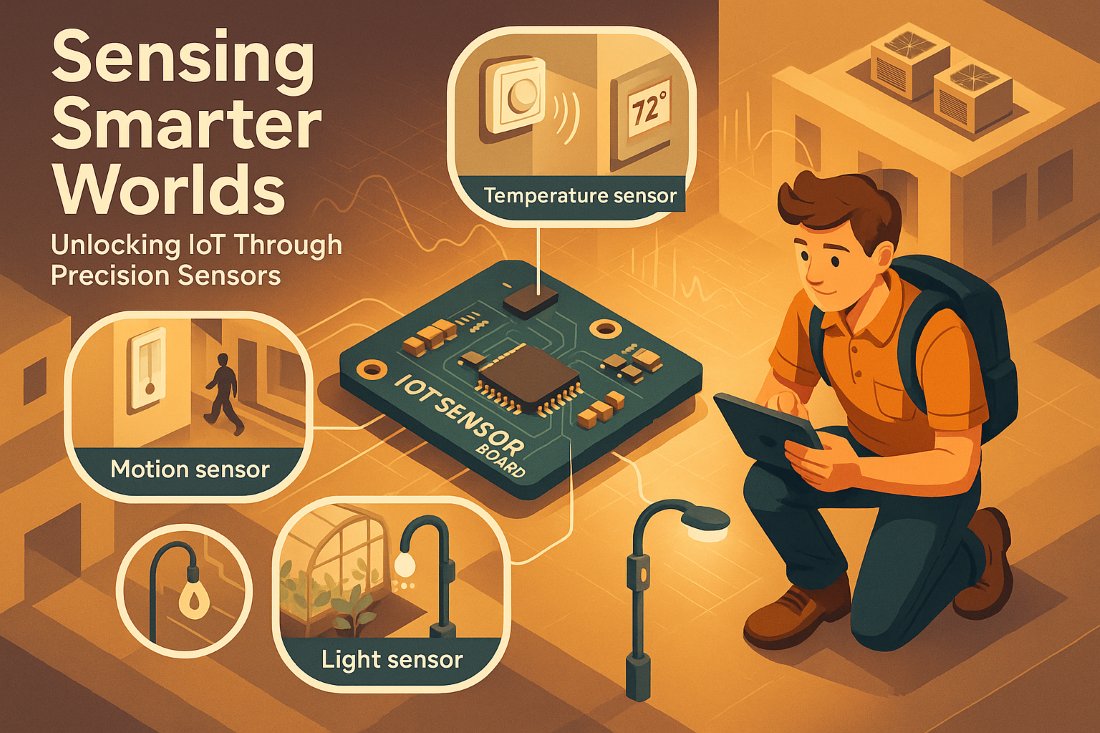
The foundational component in any IoT ecosystem is a sensor. Typically, these sensors are embedded in IoT devices which can be mechanical machines, consumer products, or digital objects. They collect data from the environment such as motion, humidity, temperature, and light for later analysis. To make any IoT environment functional, total reliability and accuracy of these sensor devices is absolutely vital.
In recent times, there has been great improvement in sensor technology that has allowed IoT sensors to collect diverse data with tremendous accuracy. Modern sensor technology can ensure great precision in data collection and can record even minute changes in a particular environment. This much improved sensor capability has taken the effectiveness of IoT applications to another level.
2. Connectivity: Enabling Trustworthy Communication
After sensors, connectivity is the second most important technology that makes IoT work. Once the data is collected, it must be smoothly transferred across the systems and devices. It is essential for an IoT environment to have dependable communication channels to make sure that the information recorded by sensors gets stored at the desired location for further processing and analysis. IoT engineers have numerous options such as bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and cellular networks.
Your choice of connectivity option would primarily depend on the main requirements of an IoT application like data rate, power consumption, and range. To make sure that communication between IoT systems is smooth and non-disruptive, connectivity must be trustworthy and secure. The IoT environment can also get vulnerable to diverse cyber threats. Thus, integrating reliable communication channels make sure that IoT devices remain secure from malware and unauthorized access.
3. Data Processing: Robust Analysis and Data Protection
Now, in an IoT environment, once the data has been collected and stored in the IoT cloud, we need robust data processing solutions to process and analyze the data and derive effective insights. Data processing, as one of the components of IoT, involves all the tools, computational techniques, and algorithms required for data analysis and interpretation.
This processing of data results in remarkable insights that yield intelligent decisions, competitive edge, and improvement in operational efficiency. Depending on the need of the application, it can be further divided into two categories: cloud processing and edge processing.
- Edge Processing- Edge processing is basically needed in applications where quick response and immediate decision making is crucial. For example, in industrial automation and automatic vehicles, IoT systems can respond to environmental changes in real-time and minimize the load on network infrastructure. Since data is processed locally, bandwidth and latency is also reduced in edge processing.
- Cloud Processing- In cloud processing, more storage capacity and computational power is necessary, and thus it is more suitable for applications requiring long-term use of data or data analysis on a massive scale. Moreover, IoT systems need a cloud environment that can support these huge data requirements and intricate analytical processes. For higher-end applications like healthcare systems and smart cities, cloud processes are required.
4. User Interface: How Can a User Interact with IoT?
After processing of data is done, IoT needs to create an output. And, for this output, there is a need for an interface using which the end-user can interact with the IoT environment. Now, essentially, any IoT system contains a user-friendly platform using which users can track system performance, visualize data collected by IoT sensors, and administer all the connected devices.
A well-developed user interface is key to an IoT solution because it is where a user can access and interpret any data. The user interface can be anything ranging from simple smartphone apps, AI voice assistants, web dashboard, and even automatic doors connected with biometric systems. Users need an interface to understand updates in the system, get alerts, control the environment, or make smart decisions in real-time.
Conclusion
IoT allows digital systems to track, monitor, and modify each interaction in real-time without any need of human intervention. The components of IoT are the essential building blocks that enable seamless data flow, automation, and smart functionality across connected systems.. This blog explores the components of IoT in detail and explains how data travels from sensors, to cloud, and then becomes available in the user interface. For more information on IoT, how IoT works, and real-life applications of IoT, explore our blog section!