In today’s hyperconnected online landscape, the Internet of Things (IoT) significantly transforms how devices communicate, collect, and exchange data. But have you ever wondered how IoT devices communicate with one another? Let’s face it, behind every data exchange lies a complex network of communication protocols that makes all the difference. Among the plethora of IoT protocols available, one such robust and reliable protocol is the AMQP protocol in IoT ecosystems. AMQP refers to Advanced Message Queuing Protocol designed for distributed networks. This serves as the foundation for enterprise-level IoT devices, which protects their reliability and credibility.
With the billions of IoT devices building together complex networks, the need for powerful messaging protocols becomes crucial. Whether you are a developer or system architect, these protocols not only streamline communication but also safeguard the integrity and security of these networks. Let’s decipher what AMQP is and the need for the AMQP protocol in IoT, including their challenges and real-world use cases. Additionally, you will also learn AMQP vs other IoT protocols---how it is different and their future scope in the IoT ecosystem.
What is the AMQP Protocol in IoT?
AMQP is an acronym which stands for Advanced Message Queuing Protocol. This is an open standard protocol for massage-orientated middleware, used to encrypt messages for secure communication. The protocol was originally developed by financial institutions for secure, robust, and definitive messaging among distributed networks. It ensures seamless communication and data exchange between IoT devices regardless of platform and vendors, even under challenging network conditions.
Over time, with the rise of advanced technologies and increasing needs of distributed systems, it became a versatile protocol. Meanwhile, the AMQP protocol in IoT supports current IoT communication demands and current industry requirements. Therefore, it can manage massive volumes of data across a wide range of industries without having to worry about data loss.
Why does the AMQP protocol in IoT matter?
One of the common benefits of the AMQP protocol is its reliability and flexibility. IoT systems often dealt with large amounts of data from thousands of distributed systems and sensors in IoT. Hence, a sophisticated communication protocol is essential for seamless, secure, and reliable data exchange. AMQP stands out as a game-changer solution, providing robust features like reliable message delivery, asynchronous communication, and priority-based routing. Let’s discuss the benefits of using AMQP protocols over other simple protocols.
- Guaranteed Message Delivery: With assured message delivery, AMQP comes with automatic message acknowledgement and queuing features while ensuring no data loss during data transmission.
- Flexible Architecture: AMQP offers flexible architecture because it supports a wide range of messaging patterns, like the publish-subscribe model, broadcasting messaging, and point-to-point.
- Security-enabled Designs: With the increasing concern of data breaches and cyberthreats, it utilizes SSL/TLS encryption and SASL authentication to ensure secure sensitive data transmission.
- Interoperability: The open standard nature of AMQP makes it cross-platform and enables integration with third-party applications. This allows you to integrate with Azure and AWS cloud platforms and use ARM Cortex and Raspberry Pi technologies.
These extensive benefits make it a must-have protocol for healthcare, industrial automation, smart city applications, and more.
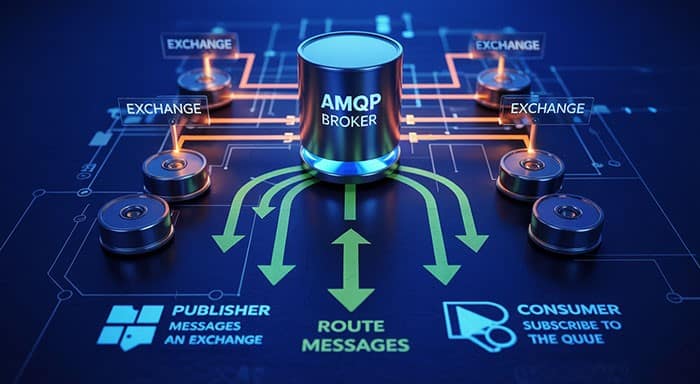
Components of AMQP in IoT
- Exchanges: Exchanges are entities where producers publish the message, fetch, receive, and store messages in the right queue. The AMQP protocol in IoT supports 4 types of exchanges: Headers, Fanout, Topic, and Direct, having different mechanisms to route the message.
- Channel: It refers to a multiplexed virtual connection between an AMQP producer and consumer within an existing physical connection. Channels ensure effective communication is established among brokers and clients.
- Massage Queue: Massage Queue is the place where messages are stored until they are safely sent or pointed to the receiver. Consumers receive messages based on priority or the first come, first served (FCFS) principle.
- Binding: Bindings are the entities that connect and establish relationships between queues and exchanges. Binding determines how messages are filtered and transmitted to the broker based on the predefined rules.
- Virtual Host: Virtual host (vhost) is a platform that provides segregated capabilities within the same broker. Based on the user and their access rights, multiple vhosts can work at the same time with different sets of exchanges, queues, and bindings.
How AMQP Stands Out from Other Protocols?
When choosing messaging protocols for IoT devices, it is important to understand how it is different from other IoT protocols like MQTT and CoAP. While they are popular and widely used protocols, they serve different purposes. Let’s understand AMQP vs MQTT vs CoAP: how they are different from each other.
| AMQP | MQTT | CoAP |
| Supports both point-to-point and publish-subscribe models, ideal for complex enterprise integration. | Primarily, a public-subscriber model for simple M2M architecture in IoT and low-level organization | Uses a request response model like HTTP, ideal for constrained networks and devices |
| Supports both client-server and client-broker architecture | It only support client-broker architecture | Support mainly client-server architecture |
| AMQP provides robust messaging features, including guaranteed message delivery, message queuing, and transaction support | Support lightweight messaging with fewer delivery guarantees and limited message routing capabilities | Offers lightweight messaging using RESTful methods with optimized dependency on UDP and DTLS |
| Offers comprehensive security features like authentication, access control, and encryption | Provide basic security measures typically relies on fundamental network security like TLS | Provide security measures like DTLS (datagram transport layer security) for controllable devices |
| Focuses on high interoperability regardless of system and vendors, ideal for enterprise-scale environments | Designed for IoT interoperability, suitable for minimal bandwidth and low power usage systems | Built for interoperability within a limited environment, perfect for restricted communication |
AMQP, MQTT, and CoAP are all designed for message-orientated protocols, but they serve different functionalities and cases. The better choice often depends upon particular requirements. If you are running a large organization and require complex routing, reliable message queuing, and transactional support, AMQP protocol in IoT can be an effective solution.
Conclusion:
As the IoT ecosystem is rapidly growing, the need for a robust and reliable messaging system has become essential. AMQP protocol in IoT is renowned as a powerful, secure, and scalable option for developers and system architects aiming to streamline device communication. With its extensive range of features like handling massive amounts of data, guaranteed message delivery, and advanced routing support, it quickly became a must-have protocol among available messaging protocols. This article comprehensively discussed the AMQP protocol in IoT environments with its key components and importance. Additionally, it also explained how it is different from other messaging protocols. Now, we hope you have a brief knowledge about it---it's time to implement the AMQP protocol in your project.
Related Posts
DDS Protocol in IoT: Features, Architecture, Working, and Applications