The systematic building of educational and training programs to improve learning is called instructional design (ID). It involves designing instructional delivery Type and content that could be understood and well presented in a manner that is appealing to the learner.
The Benefits of Instructional Design in Schools and Businesses
Instructional design is very important in educational as well as business environments. In discussing training, it is imperative to assess training programs that could ensure the fulfillment of learning outcomes. Employers need to make appropriate changes necessary for professional training courses for the employee’s skills and productivity to be raised. The latter makes it easier for schools to adapt lessons to the needs of students, and improve the process of acquisition and consolidation of knowledge.
Maximize the Return on Your LMS Investment with Company Raccoongang
Ensure your Learning Management System (LMS) is more than just a repository of content. Partner with Raccoongang’s instructional design consultants to create tailored courses that meet your specific needs, boosting both learner engagement and ROI.
Proven Benefits of Instructional Design
- Enhanced Course ROI: Instructional design can improve the return on investment of courses by 50-60%, making it a crucial strategy for any learning initiative.
- Project Success: Effective instructional design contributes 30-40% to the success of an eLearning project, highlighting its role in achieving educational goals.
- Faster Completion Rates: By streamlining content and aligning it more closely with learner needs, instructional design can reduce course completion times by 35-45%.
The Foundations of Instructional Design
The instructional design effect is anchored in cognitive psychology and educational theory. Here are some couple of key theoretical frameworks instructional designers work with:
- Behaviorism looks at how behavior changes after learning and stresses the importance of outside influences and rewards.
- Cognitive theory looks at the mental processes that go into learning, like remembering, thinking, knowing, and fixing problems.
- Conceptualism says that students build their own knowledge and understanding of the world by doing things and thinking about what they did.
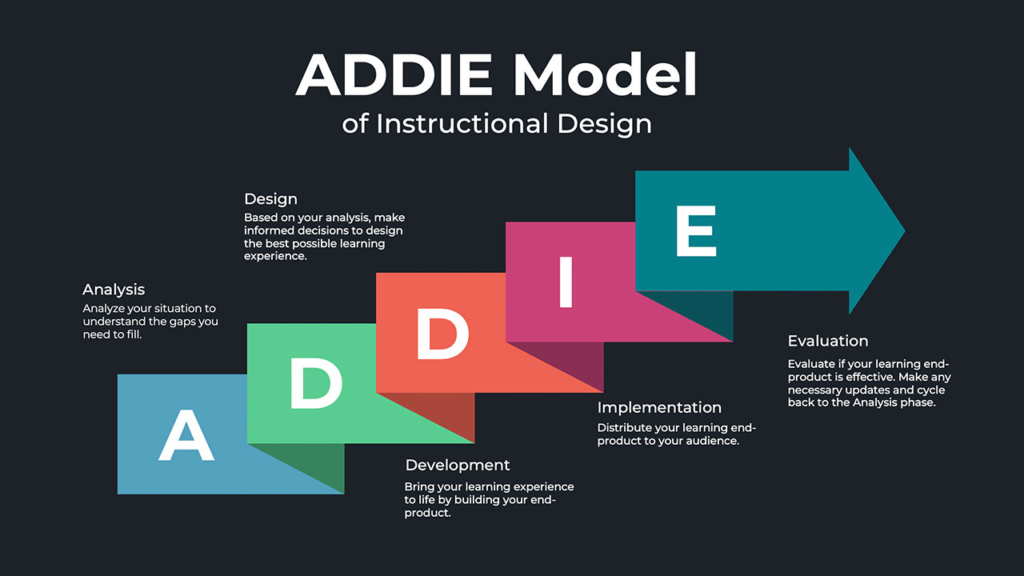
Instructional Design Steps
The five-phase ADDIE model summarizes the instructional design process: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation.
1. Analysis
This step is related to the problem of learning or a set of problems, the goals of an intervention, and the analysis of current knowledge and skills. The main tasks in this phase are:
- Needs analysis: The attempt to identify what it is that the learners need to learn.
- Learner analysis: Understanding who the learner is and what he or she previously knows.
2. Design
In this phase, the instructional designers would outline the learning goals and objectives and pick the content, teaching materials, and learners’ activities that would best meet those goals and objectives. This phase may involve:
- Storyboarding: A plan that arranges the sequence of content delivery.
- Strategy Development: Selection of the methodologies to be used in the presentation of content.
3. Develop
Content Designers create and build the resources that have been specified by the design, which may include:
- Content creation can include writing lectures, making videos, and creating simulations.
- Choice of tools: Identifying the technology or combination of technologies that will be used to deliver the content.
4. Implement
The implementation phase is when the course or training is actually delivered to the target audience. This phase involves considerations of:
- Pilot testing: conducting a test session with a small group of individuals to get their responses.
- Full-Scale Implementation: Delivering the intervention to the target population.
5. Evaluate
Value Evaluation is meant to determine the effectiveness and efficiency of the instructional design. It has two parts:
- Formative Evaluation: The evaluation undertaken during the design and development to refine the educational program.
- Summative Assessment: The assessment, carried out after the execution of the project, decides on the impact and whether the learning objectives have been met.
Impact and Application
The contexts in which it is applied may vary; they can range from normal classroom teaching to corporate training and online tutorials. Instructional designers, when following some principles of instruction design, are found to create resulting learning experiences of significance and meaning for the learners at hand.
As the advancement of learning and training is heading towards the future, the instructional design shapes as the keystone in constructing efficient environment for the learning process.
This is accomplished through the binding of theoretical and applied content, along with continuous evaluation as instructional design is used to guarantee educational solutions address the needs of students, and coincide with the objectives of organizations. This learning manual situates instructional design as knowledge transmission and how learning can be made systematic, exciting, and valuable.
Also Read
Stay updated by signing up for our newsletter
Read our full Privacy Policy here.




