In recent years, technology has been growing rapidly, and everyone depends on these advanced technologies for their convenience. The IoT (Internet of Things) has become an effective part of our lives, which continues to change the way we interact with technology. IoT is transforming various fields, from smart homes and self-driving cars to industrial automation and healthcare. This technology reduces human intervention by automating tasks like home automation devices for controlling the lights and fans, wearable devices for tracking fitness and simplifying tasks, driverless cars, automatic traffic systems, etc.
Have you ever wondered how does IoT works and how it automates the tasks? The answer lies in large and comprehensive infrastructure—IoT architecture— involving multiple layers and elements. IoT architecture provides different solutions tailored to different tasks that create the foundation of an ecosystem that emphasizes seamless connectivity. In this article, we will describe IoT in detail, its architecture, layers, components, advantages and disadvantages of IoT architecture in developing an IoT solution
What Is IoT Architecture?
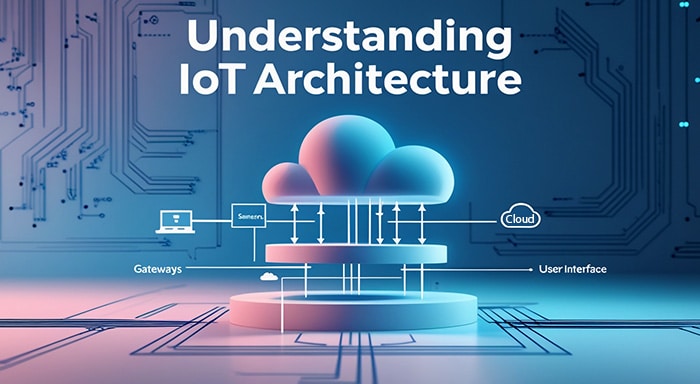
The IoT is a sophisticated network of connected physical devices embedded with sensors and actuators that share and exchange data over the network. IoT architecture is the structural framework made up of multiple layers, enabling devices and networks to work together in the IoT ecosystems. The architecture is commonly divided into several layers, which define how data is exchanged between sensors, cloud platforms, end users, and gateways. It enables the network to have flexible, secure, and seamless data processing and makes the foundation of an IoT solution.
Key Layers of IoT Architecture:
The IoT architecture mainly consists of 4 important layers, each with different roles and purposes. Below is the detailed breakdown of each layer:
Perception Layer:
The perception layer is the initial layer of IoT architecture that involves physical IoT devices like sensors and actuators to gather raw data from the environment. This layer serves as the interaction between the physical world and the ecosystem. This layer includes pressure, temperature, and motion sensors and converts them into digital signals. actuators in IoT are used to transform energy into motion, which instructs devices to perform tasks based on the data gathered by sensors and additional commands given by the user.
Network Layer:
The network layer, also known as the transport layer, ensures data flow within the network. This layer transfers the data collected by the perception layer to the processing layer through various communication technologies such as WiFi, Bluetooth, MQTT, HTTP, Zigbee, and cellular 4G/5G networks. Additionally, this layer uses gateways to bridge the gap between devices and cloud platforms across the network.
Processing Layer:
The data processing layer interprets and analyzes the data to help businesses to streamline their processes. This layer processes raw information from cloud platforms through advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, and big data analytics in order to process and restrain valuable insights that are used for automation and decision-making.
Application Layer:
The application layer is the final layer in IoT architecture where processed data is ready to interact with humans. This layer allows devices to provide actionable insights,, such as mobile apps, web platforms, and centralized dashboards that offer actionable insights. This layer is responsible for providing user-friendly reliable information to users or specific industries like industrial automation, smart cities, healthcare, and also IoT in agriculture.
What Is IoT | History, Benefits of IoT?
Challenges in Developing IoT Architecture
There are several challenges faced by IoT developers while creating an effective IoT architecture. Here are some challenges:
- Data Security: Preventing the devices and data from potential cyberattacks and secure data exchange is a major challenge in the IoT ecosystem.
- Reducing Latency: Applications based on real-time features require minimal delays in data transfer.
- Device Interoperability: In the IoT network, combining devices for different purposes raises compatibility issues.
- Scaling Efficiency: Careful planning is essential for designing systems without affecting performance.
- Managing Data Volume: The major challenge in IoT architecture is to store and process large volumes of data gathered by IoT sensors.
Conclusion
In today’s modern era, rapid advancement in IoT architecture is playing a pivotal role in shaping the world for connectivity and innovation. IoT architecture is crucial in achieving the seamless functioning of interconnected devices and systems in the network. Understanding the meaning of IoT architecture, its core layers, and the potential challenges of IoT is required to create efficient, secure, and future-ready solutions. This includes several components of IoT such as sensors and devices that ensure seamless data transfer, and users get a seamless user experience through these devices.